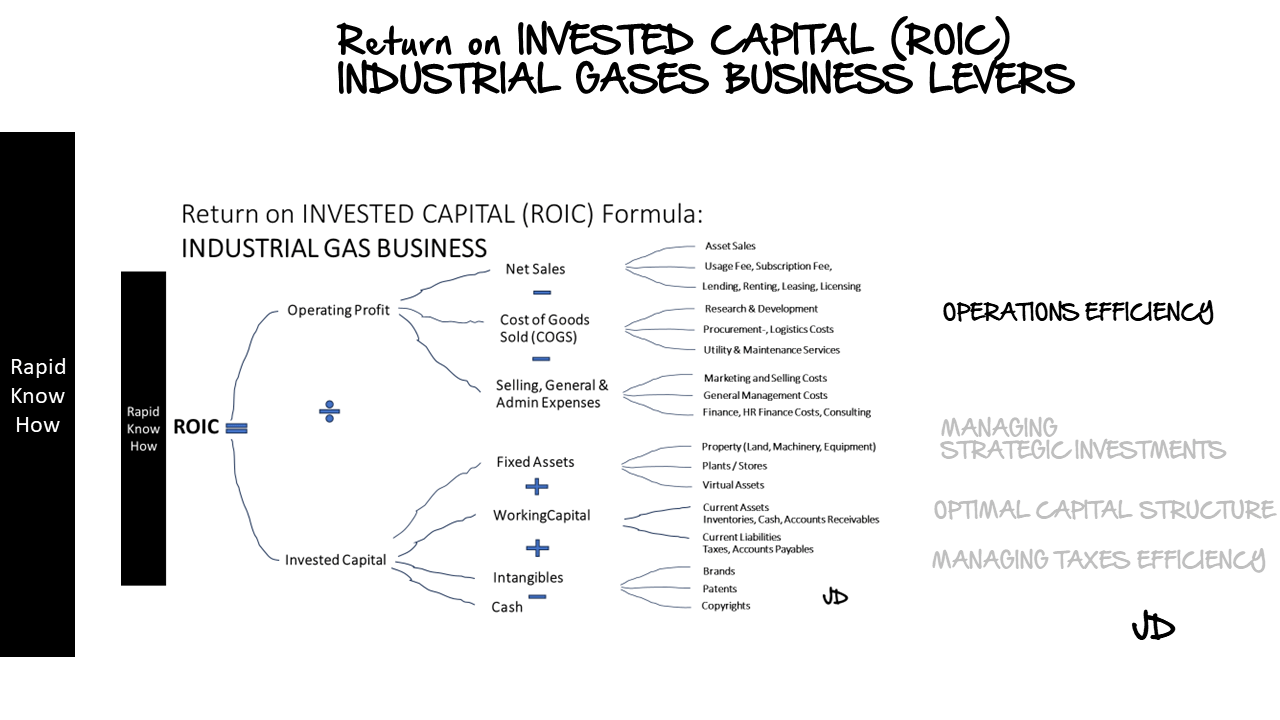
RapidKnowHow > Due Diligence Model for Industrial Gases in Excel Step-by-Step
Creating a Due Diligence Model for the Industrial Gases sector in Excel involves several detailed steps.
Below is a comprehensive guide to building this model step-by-step, focusing on key elements, formulas, and best practices.
Step 1: Define the Purpose of the Model
Identify the objectives of your due diligence model:
- Assess the financial viability of potential investments or acquisitions.
- Analyze the risk factors associated with the industrial gas market.
- Estimate future revenue, expenses, and net income based on various scenarios.
Step 2: Gather Necessary Data
Collect relevant data required for your model:
- Historical financial data of target companies (if available).
- Industry growth rates, pricing trends, and cost structures.
- Market research reports, regulatory information, and competitor analysis.
Step 3: Set Up Your Excel Workbook
Create a new Excel workbook with the following sheets:
- Assumptions
- Calculations
- Outputs
- Scenarios
- Sensitivity Analysis
Step4: Input Key Assumptions
Sheet: Assumptions
Here, you will define variables that will drive the financial model. Example layout:
| Variable | Optimistic | Base Case | Pessimistic | |———-|————|———–|————-|
| Annual Demand Growth Rate (%) |7% |4% |1% |
| Average Selling Price ($/unit) | 1500 |1400 |1300 |
| Variable Cost ($/unit) |600 | 650 |700 |
| Fixed Costs ($) | 500,000 |520,000 | 550,000 |
| Initial Units Sold | 100,000 |100,000 | 100,000 |
Step 5: Build the Calculations Sheet
Sheet: Calculations
Create formulas to estimate revenue, costs, and profit. Example structure:
- Revenue Calculation:
- Formula: [ \text{Revenue} = \text{Units Sold} \times \text{Selling Price} ]
- Costs Calculation:
- Total Costs:
- Formula: [ \text{Total Costs} = \text{Fixed Costs} + (\text{Variable Cost} \times \text{Units Sold}) ]
- Net Income Calculation:
- Formula: [ \text{Net Income} = \text{Revenue} – \text{Total Costs} ]
Example layout of the calculations sheet: | Scenario | Revenue ($) | Total Costs ($) | Net Income ($) | |—————-|—————-|—————–|—————–|
| Optimistic | =B2B6 | =B3+B4B6 | =B8-B9 |
| Base Case | =C2C6 | =C3+C4C6 | =C8-C9 |
| Pessimistic | =D2D6 | =D3+D4D6 | =D8-D9 |
- Replace B2, B3, B4, and B6 in formulas with the respective cell references from the Assumptions sheet.
Step6: Create the Outputs Summary
Sheet: Outputs
Summarize the results here for easy referencing. Use formulas from the Calculations sheet to populate this summary.
Example layout: | Scenario | Revenue ($) | Total Costs ($) | Net Income ($) | |—————-|—————-|—————–|—————–|
| Optimistic | =Calculations!B8 | =Calculations!B9 | =Calculations!B10 |
| Base Case | =Calculations!C8 | =Calculations!C9 | =Calculations!C10 | | Pessimistic | =Calculations!D8 | =Calculations!D9 | =Calculations!D10 |
Step7: Set Up Scenarios
Sheet: Scenarios
This sheet enables you to manage different sets of assumptions effectively. Use Excel’s Scenario Manager to define various scenarios based on the inputs you established in the Assumptions sheet.
Step8: Sensitivity Analysis
Sheet: Sensitivity Analysis
Evaluate how changes in key variables affect net income. This can be done using Excel’s Data Table feature or scenario analysis. Set up a simple table to vary inputs like selling price, variable costs, and demand growth.
Example layout: | Variable | Change (%) | Net Income from Optimistic | Net Income from Base Case | Net Income from Pessimistic | |————————–|————|—————————–|—————————|——————————|
| Selling Price | +10 | =Optimistic!B10 + 10% | =BaseCase!B10 + 10% | =Pessimistic!B10 + 10% |
| Variable Cost | -10 | =Optimistic!B10 -10% | =BaseCase!B10 -10% | =Pessimistic!B10 -10% |
| Demand Growth Rate | +5% | =Optimistic!B10 * (1 +0.05) | =BaseCase!B10 * (1 +0.05) | =Pessimistic!B10 * (1 +0.05) |
Step9: Final Review and Adjustments
- Review the entire model for accuracy and consistency.
- Make sure to include comments where necessary for clarity, especially in complex formulas.
- Format the sheets neatly: use conditional formatting to highlight key metrics and results.
Step 10: Documentation
Document the methodology, assumptions, and insights from the model in a separate sheet or a report. This will help stakeholders understand the model and the reasoning behind the assumptions used.
Conclusion
This step-by-step guide enables you to construct a structured and comprehensive Due Diligence Model for the Industrial Gases sector in Excel.
By meticulously inputting data, creating formulas, and analyzing scenarios, you can derive valuable insights that inform strategic investment decisions.