**The Business Leader Quadrant: A Framework for Understanding Business Dynamics**
The Business Leader Quadrant is a conceptual framework that helps organizations and business leaders understand their positioning in the market based on two primary dimensions: market size and stakeholder value.
This model categorizes businesses into four distinct quadrants, each representing a unique combination of market focus and value proposition.
By analyzing these quadrants, leaders can better strategize their operations, align their goals, and ultimately enhance their competitive advantage.
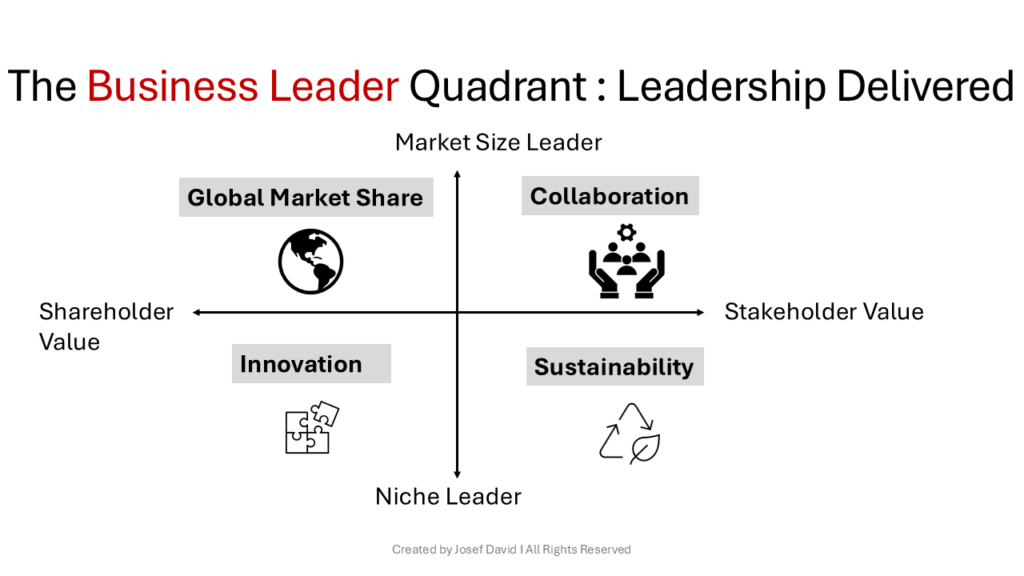
1. Market Size Leader – Shareholder Value: Global Marketshare Leader
In this quadrant, businesses prioritize capturing a large share of the overall market while focusing on maximizing shareholder value. Companies in this category often operate on a global scale or within expansive geographical regions. Their strategies are typically centered around aggressive marketing, economies of scale, and operational efficiencies that allow them to dominate the market.
For instance, multinational corporations like Coca-Cola or Procter & Gamble exemplify this quadrant. They leverage their vast distribution networks and brand recognition to maintain a significant presence across various geographies.
The emphasis here is on profitability and return on investment for shareholders, often leading to strategies that prioritize short-term financial performance.
2. Market Size Leader – Stakeholder Value: Collaboration Leader
Businesses in this quadrant also aim for a large market share but place greater emphasis on stakeholder value through collaboration. These organizations recognize that long-term success is not solely dependent on shareholder returns but also on building relationships with customers, employees, suppliers, and the community at large.
Companies like Unilever or Salesforce exemplify this approach. They actively engage in partnerships and collaborations that foster innovation and create shared value among all stakeholders.
By prioritizing collaboration, these businesses can adapt more readily to changing market conditions while ensuring that their growth benefits a broader range of constituents beyond just shareholders.
3. Market Niche Leader – Shareholder Value: Innovation Leader
This quadrant is characterized by businesses that focus on niche markets while emphasizing innovation as a means to drive shareholder value. Companies here often invest heavily in research and development to create unique products or services that cater to specific customer needs within their niche.
An example of this would be Tesla in the automotive industry. By concentrating on electric vehicles and sustainable energy solutions, Tesla has carved out a significant niche while simultaneously delivering substantial returns to its investors through innovative technology and strong brand loyalty.
The focus on innovation allows these companies to differentiate themselves from competitors and maintain pricing power within their specialized markets.
4. Market Niche Leader – Stakeholder Value: Sustainability Leader
In this final quadrant, businesses not only target niche markets but also prioritize sustainability as a core component of their stakeholder value proposition. These organizations understand the importance of environmental stewardship and social responsibility in today’s business landscape.
Companies like Patagonia or Beyond Meat exemplify this approach by integrating sustainable practices into their business models while serving specific consumer segments concerned with ethical consumption.
Their commitment to sustainability resonates with customers who are increasingly making purchasing decisions based on environmental impact, thus creating loyalty and long-term relationships that benefit both the company and its stakeholders.
Conclusion
The Business Leader Quadrant provides a valuable framework for understanding how different companies position themselves within the marketplace based on their focus on market size versus niche markets, as well as their commitment to shareholder versus stakeholder value.
By analyzing where an organization fits within these quadrants, business leaders can develop targeted strategies that align with their goals—whether it’s maximizing shareholder returns through geographical expansion or fostering collaborative relationships for sustainable growth.
Ultimately, understanding these dynamics can help leaders navigate the complexities of modern business environments while ensuring they remain responsive to both market demands and societal expectations.
As businesses continue to evolve in response to changing consumer preferences and global challenges, frameworks like the Business Leader Quadrant will be essential tools for guiding strategic decision-making in pursuit of long-term success.