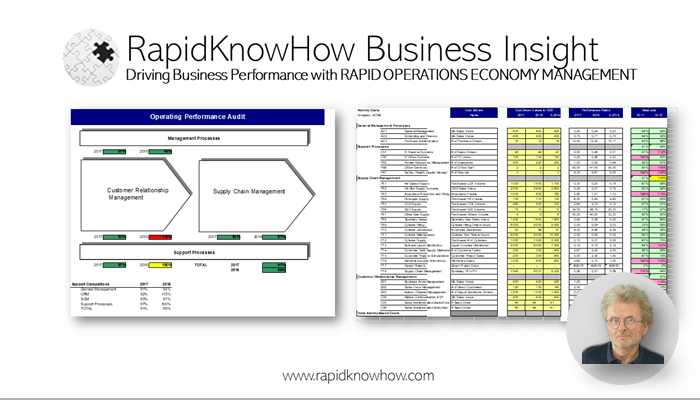
I’ll break this down clearly so you can see exactly how Activity-Based Costs (ABC) compare with Total Value Costs (TVC) in both traditional B2B business models and AI-powered business models.
1. Core Definitions
| Term | Meaning | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Activity-Based Costs (ABC) | Assigns costs to products/services based on the actual activities and resources consumed. | Accurately identifies which activities drive costs, helping to optimize or eliminate waste. |
| Total Value Costs (TVC) | Extends cost analysis beyond operations to include the full cost to deliver value — monetary, time, convenience, sustainability, and opportunity costs. | Shows the true cost of delivering value to customers, including intangible and long-term factors. |
2. Key Cost Elements
A. Activity-Based Costs (Traditional Focus)
- Direct labor (time spent producing or serving)
- Materials and resources
- Overhead by activity (admin, logistics, QA)
- Customer service (per interaction)
- Sales & marketing (per lead/customer)
B. Total Value Costs (Extended Focus)
- All ABC elements+:
- Customer acquisition and retention costs
- Time-to-value (speed from purchase to customer result)
- Opportunity cost of slow delivery or poor UX
- Sustainability cost/impact (CO₂ footprint, waste)
- Innovation cost (R&D, tech upgrades to keep value competitive)
- Risk mitigation cost (security, compliance, geopolitical)
3. Comparative View: Traditional B2B vs AI-Powered B2B
| Dimension | Traditional B2B (ABC) | AI-Powered B2B (ABC) | Traditional B2B (TVC) | AI-Powered B2B (TVC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost Scope | Operations-focused | Operations + partial automation | Includes operational + intangible costs | Full-spectrum costs including speed, convenience, sustainability |
| Cost Drivers | Labor, materials, manual processes | AI-assisted labor, reduced manual work, cloud services | Same as ABC + customer-side time, market delays | AI reduces customer time, improves market speed, optimizes sustainability |
| Overhead Impact | High (manual coordination) | Lower (automation, AI-driven workflows) | Still high due to slow adaptation | Lower due to continuous AI optimization |
| Customer Value Link | Weak — cost measured internally | Moderate — cost linked to faster processes | Stronger — includes customer perception | Strongest — includes value-based pricing, experience, retention |
| Strategic Advantage | Limited cost efficiency | Moderate cost efficiency + speed | Limited differentiation | High differentiation via value per cost unit |
| Example | Gas supply: costs tied to truck deliveries, manual order management | Gas supply: predictive AI for refills, route optimization | Includes downtime costs to customer, slow refill penalties | Includes eliminated downtime, improved ESG score, faster service ROI |
4. Impact on Decision-Making
- ABC in Traditional B2B → Helps cut waste in internal processes but doesn’t reveal the full economic picture for customers.
- TVC in AI B2B → Aligns pricing and investments with customer-perceived value, enabling value-based pricing and stronger competitive position.
5. Practical Example – Industrial Gas
Scenario: Delivering medical oxygen to hospitals.
- ABC:
- Labor hours for drivers
- Cylinder filling costs
- Truck fuel and maintenance
- Dispatch center operations
- TVC:
- Downtime cost to hospital if delivery late
- Carbon footprint of delivery
- Opportunity cost if competitor delivers faster
- AI-driven route optimization benefit
- Predictive supply preventing emergency orders
AI model allows factoring TVC savings into pricing and marketing, justifying premium positioning and licensee network expansion.
6. Strategic Takeaways
- ABC is still essential for internal cost control, but alone it’s too narrow.
- TVC lets you quantify strategic advantage and customer ROI — critical in AI-driven ecosystems.
- In AI-powered B2B, TVC should become the main cost lens because:
- AI shortens time-to-value
- AI enables value-based pricing
- AI optimizes sustainability metrics customers now care about
- Shifting from ABC-only to TVC-first changes your business from cost-cutter to value-maximizer.
Comparing Activity-Based Costs (ABC) and Total Value Costs (TVC) in B2B Models
1. Core Concepts
- Activity-Based Costs (ABC) – Measures the cost of delivering products and services based on the actual activities and resources used.
- Total Value Costs (TVC) – Extends beyond operational costs to include the full cost of delivering value, such as customer time, convenience, sustainability, innovation, and risk management.
2. Key Differences
| Metric | Traditional B2B (ABC) | AI-Powered B2B (TVC) | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost Scope | Operational only | Full value chain, including customer-side costs and ESG factors | Broader coverage, better strategic insight |
| Main Cost Drivers | Labor, materials, logistics | AI automation, predictive demand, ESG compliance | AI reduces waste and labor intensity |
| Customer Value Link | Weak – focused on internal costs | Strong – integrates time-to-value, convenience, and sustainability | Stronger loyalty, higher pricing power |
| ROICE | +12% | +38% | +26 percentage points |
3. Quick Insights
- ABC improves internal efficiency but misses many customer-side value drivers.
- TVC incorporates the complete cost-to-value equation, enabling value-based pricing.
- AI-powered models leverage automation, prediction, and sustainability tracking to reduce hidden costs and accelerate value delivery.
4. Strategic Takeaway
Shifting from ABC-only to TVC-first in an AI-powered model can increase ROICE by 20–30 percentage points.
The main drivers are:
- Faster time-to-value
- Reduced hidden costs
- Increased customer loyalty and premium pricing potential
Comparing the Competences of the Traditional Value Chain and the AI Powered B2B Value Chain
Here’s a structured Traditional B2B vs AI-Powered B2B Value Chain comparison — showing where competencies become obsolete and which new ones are required.
1. Value Chain Category Comparison
| Value Chain Category | Traditional B2B Model | AI-Powered B2B Model | Obsolete Competences | New Competences |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inbound Logistics | Manual procurement, fixed suppliers, batch deliveries | AI-optimized sourcing, dynamic supplier networks, just-in-time replenishment | Manual purchasing clerks, static supplier management | AI-driven supplier analytics, real-time sourcing optimization |
| Operations | Manual workflows, siloed systems, reactive quality control | AI automation, predictive maintenance, digital twins | Paper-based scheduling, reactive issue handling | AI workflow orchestration, predictive operations management |
| Outbound Logistics | Fixed delivery routes, manual dispatch, bulk shipments | Predictive routing, demand-based delivery scheduling | Route clerks, static logistics planning | AI route optimization, last-mile predictive logistics |
| Marketing & Sales | Cold calling, trade shows, manual CRM updates | AI-driven lead scoring, personalized campaigns, automated CRM | Generic lead generation, mass mailing | AI marketing analytics, personalization algorithms |
| Service | Reactive support, manual ticketing | AI-powered chatbots, predictive customer service | Call center scripts, ticket backlog management | AI conversational design, predictive service management |
| Technology Development | Slow R&D cycles, manual testing | Rapid AI prototyping, digital product twins | Sequential waterfall development | AI-accelerated innovation cycles, agile data-driven prototyping |
| Procurement | Annual supplier contracts, manual negotiations | AI contract optimization, dynamic bidding | Annual paper-based tenders | AI-powered supplier scoring, blockchain-based smart contracts |
| HR & Training (support activity) | In-person onboarding, static skills training | AI-assisted onboarding, adaptive learning paths | One-size-fits-all training | AI-based skill mapping, continuous upskilling systems |
| Finance & Control (support activity) | Monthly/quarterly reporting, manual compliance checks | Real-time dashboards, AI anomaly detection | Manual report consolidation | AI financial analytics, predictive cash flow modeling |
2. Competence Shifts — Overview
Obsolete / Declining Competences
- Manual scheduling, routing, and dispatching
- Generic, mass-market sales tactics
- Paper-based procurement and contracts
- Reactive customer service
- Sequential R&D processes without AI augmentation
- One-off, in-person training only
New / Emerging Competences
- AI-Orchestrated Operations – integrating AI into every step of logistics, production, and service
- Predictive Analytics – anticipating demand, failures, and customer needs
- Digital Twin Management – real-time modeling of products and processes
- Hyper-Personalized Marketing – algorithm-driven targeting
- Data Governance & AI Ethics – ensuring transparency, compliance, and trust
- Continuous Learning Culture – adaptive skill development supported by AI tools
- ESG & Sustainability Optimization – tracking and improving environmental/social impact with AI tools
3. Strategic Takeaway
- In Traditional B2B, many core competences are operational and repetitive — these are the ones AI will phase out.
- In AI-Powered B2B, competences are data-driven, predictive, and continuous — building competitive advantage on speed, precision, and personalization rather than scale alone.
- Leaders need to map their current value chain to the AI value chain and create a competence migration plan to replace obsolete roles with AI-era capabilities within 12–24 months.