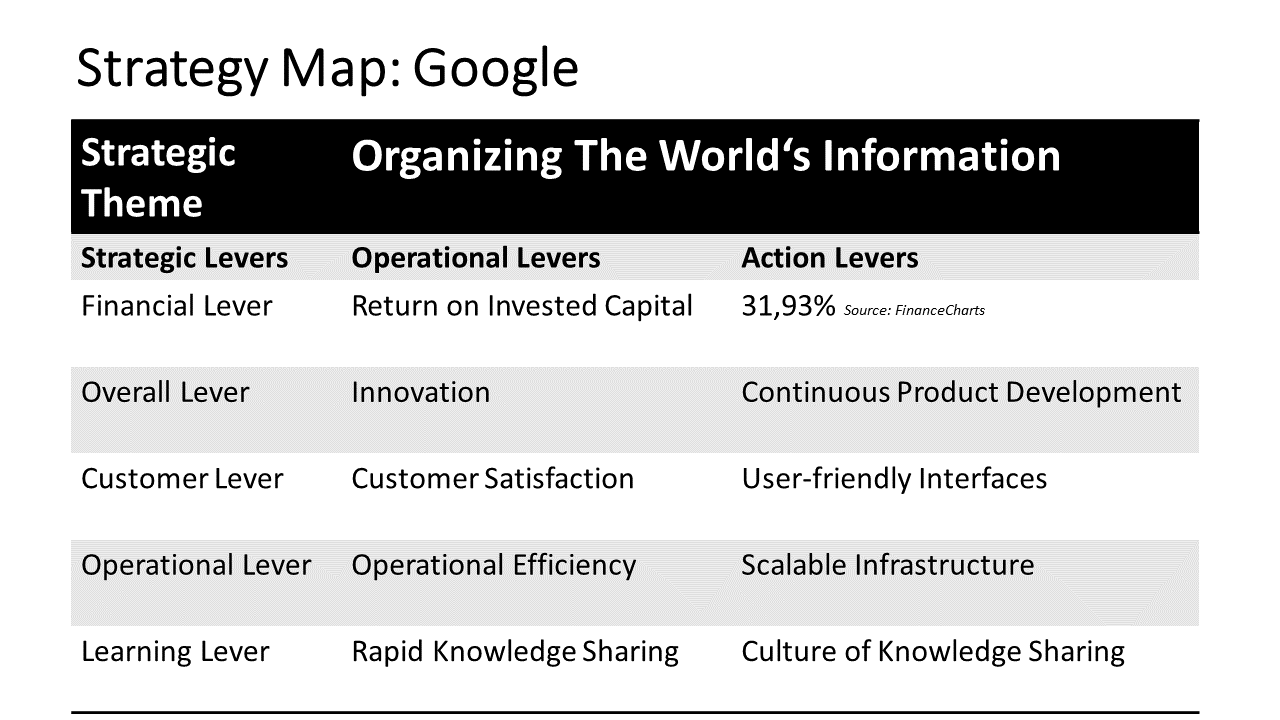
Organizational redesign focuses on restructuring the company’s framework to improve efficiency, communication, and adaptability. Managing structural complexity involves simplifying processes and clarifying roles to enhance performance and alignment with strategic goals. The Business Success Formula can be applied to evaluate how effective organizational redesign increases business success.
Application of the Business Success Formula to Organizational Redesign
- V = Value: Redesigning organizational structures effectively maximizes value by aligning resources and capabilities with strategic objectives.
- VP = Value Proposition: A streamlined organizational design enhances the company’s value proposition, allowing for quicker decision-making and better customer service.
- MU = Market Understanding: By clarifying roles and responsibilities, organizations can better respond to market changes and customer needs, strengthening their competitive position.
- SP = Strategic Partnerships: Redesigning can facilitate better collaboration across departments or with external partners, resulting in improved innovation and service delivery.
- E = Execution: Clearer structures enable more effective execution of strategies, as employees understand their roles and decision-making processes more thoroughly.
- CF = Customer Focus: Organizational redesign that prioritizes customer needs leads to better alignment of services and products, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- FM = Financial Management: A well-structured organization can optimize costs and resource allocation, leading to improved financial performance.
- T = Technology: Utilizing technology effectively during redesign can enhance communication and collaboration, supporting the new structure.
- A = Agility: A redesigned organization can respond more quickly to changes in the market, ensuring long-term sustainability and competitive advantage.
Conclusion
Managing structural complexity through organizational redesign can significantly contribute to business success by enhancing efficiency, responsiveness, and alignment with strategic goals. The Business Success Formula illustrates the positive impact of a well-structured organization on overall performance.
Examples from Different Industries
1. Healthcare: Cleveland Clinic’s Transformation
- Value (V): Cleveland Clinic restructured its organizational design to prioritize patient care, resulting in improved health outcomes and higher patient satisfaction scores.
- Value Proposition (VP): This redesign clarified roles across departments, leading to a more coordinated approach to patient treatment.
- Market Understanding (MU): The organization improved its ability to understand and meet patient needs through integrated care teams.
- Strategic Partnerships (SP): Collaborations between specialists and primary care providers were enhanced, fostering holistic patient care.
- Execution (E): Defined accountability measures improved execution of care protocols and reduced redundancy.
- Customer Focus (CF): A patient-centered approach led to more tailored care plans and better overall experiences for patients.
- Financial Management (FM): Streamlined processes reduced waste and helped manage costs effectively while maintaining high-quality care.
- Technology (T): Implementing integrated health IT systems supported better communication and data sharing among providers.
- Agility (A): The redesigned structure allowed Cleveland Clinic to quickly adapt to changes in healthcare regulations and patient expectations.
Outcome: Cleveland Clinic’s organizational redesign improved patient care quality and operational efficiency, reinforcing its status as a leading healthcare provider.
2. Manufacturing: Toyota’s Lean Manufacturing System
- Value (V): Toyota redesigned its organizational structure to adopt lean manufacturing principles, maximizing efficiency and value creation.
- Value Proposition (VP): The focus on waste reduction and continuous improvement enhanced Toyota’s reputation for quality and reliability.
- Market Understanding (MU): The redesigned structure allowed for increased responsiveness to customer feedback and market trends.
- Strategic Partnerships (SP): Toyota fostered strong relationships with suppliers, ensuring they were integrated into the lean processes.
- Execution (E): Clearly defined roles within teams improved the execution of projects and production schedules.
- Customer Focus (CF): Emphasizing customer satisfaction led to better product designs and service delivery, maintaining high levels of loyalty.
- Financial Management (FM): By cutting costs through waste reduction, Toyota improved its overall financial performance.
- Technology (T): Advancements in manufacturing technology complemented the lean processes, enhancing production capabilities.
- Agility (A): The flexible structure enabled Toyota to respond swiftly to changes in automotive market demands.
Outcome: Toyota’s lean approach and organizational redesign resulted in significant efficiencies and established it as a leader in the automotive industry.
3. Technology: Google’s Project Aristotle
- Value (V): Google restructured teams based on research from Project Aristotle, focusing on effective collaboration and team dynamics.
- Value Proposition (VP): The redesign enhanced innovation by ensuring that teams were empowered and had clear roles.
- Market Understanding (MU): Understanding the importance of team composition improved Google’s ability to foster innovation and respond to market needs.
- Strategic Partnerships (SP): Collaboration across different teams enhanced cross-functional innovation and problem-solving.
- Execution (E): The emphasis on psychological safety within teams improved execution and creativity.
- Customer Focus (CF): Teams better aligned their projects toward improving user experience and product quality.
- Financial Management (FM): Enhanced collaboration and innovation led to significant returns on investments in new product development.
- Technology (T): Utilization of collaboration tools facilitated effective communication even in the redesigned structure.
- Agility (A): The new structure allowed Google to pivot quickly in response to changing technology trends and customer feedback.
Outcome: Google’s emphasis on team dynamics and collaboration through organizational redesign led to innovation and maintained its position as a tech leader.
Conclusion
Organizational redesign by managing structural complexity is essential for achieving long-term success across various industries. The Business Success Formula demonstrates how a well-structured organization enhances value creation, execution, and customer satisfaction. The examples from healthcare (Cleveland Clinic), manufacturing (Toyota), and technology (Google) illustrate how effective organizational redesign can lead to significant improvements in performance, innovation, and profitability.