We’re exploring a fascinating and forward‑looking transformation: moving from the traditional Employee Society toward vibrant Entrepreneurial Ecosystems over the 2025–2030 period. Let’s unpack this concept and map out how such a transformation could realistically occur, drawing on emerging trends, ecosystem strategies, and innovation frameworks.
1. Why Shift from Employee Society to Entrepreneurial Ecosystems?
Employee Society typically refers to organizations structured around wage-based employment, where workers are mainly internal and roles are fixed. In contrast, Entrepreneurial Ecosystems are dynamic networks where startups, freelancers, researchers, corporates, policymakers, investors, universities, and communities co-create value through innovation, flexibility, and collaboration.
This shift is driven by:
- Digitization and Technological Disruption: Emerging technologies—AI, IoT, blockchain—demand agility and flexibility across traditional boundaries d3brk8rkzvc45n.cloudfront.netOn Digital Strategy | Dion Hinchcliffe.
- Changing Workforce Expectations: Employees nowadays seek autonomy, purpose, continuous learning, and more than just a job—they want to contribute meaningfully and innovate On Digital Strategy | Dion Hinchcliffekornferry.comPwC.
- Economic Resilience & Growth Potential: Entrepreneurial activities are powerful drivers of jobs, innovation, and inclusive economic growth. For Germany, McKinsey projects up to €2.3 trillion in value creation and 1.44 million jobs by 2030 if startup activity doubles McKinsey & Company.
- Ecosystem Revenue Potential: By 2030–2035, ecosystem-based models (e.g., home ecosystems, integrated platforms) could command 30% of global economy, over 40% of profits, and become a dominant economic structure McKinsey & Company.
2. What Is an Entrepreneurial Ecosystem?
These ecosystems are interconnected communities of actors (startups, corporates, academia, investors, policymakers) that support innovation and value creation.
Key pillars include:
- Access to Talent & Knowledge – via universities, research institutions, entrepreneurial education.
- Funding & Capital Channels – early-stage to scale-up investment pathways.
- Infrastructure & Market Access – physical/virtual spaces, digital platforms, regulatory support.
- Cultural and Social Support Structures – mentorship networks, accelerators, community platforms.
- Policy and Governance Enablers – streamlined administrative processes, supportive regulations, strategy alignment.
Examples:
- The Quantum Entrepreneurship Lab by TUM integrates technical and business students across disciplines to bridge research and startup creation d3brk8rkzvc45n.cloudfront.net+12arXiv+12Walton Family Foundation+12GEM Global Entrepreneurship Monitor+3kornferry.com+3AIHR+3.
- McKinsey’s ecosystem economy framework shows how platforms in various sectors orchestrate end-to-end journeys—like real estate, finance, and digital services McKinsey & Company.
3. Vision 2025–2030: Phased Transformation Strategy
Phase I (2025–2026): Foundation and Hybridization
- Hybrid Workforce Platforms: Blend traditional employee roles with freelancers, contractors, research partners, and gig contributors—as seen in “workforce ecosystems” MIT Sloan Management Review.
- Promote Citizen Innovation: Encourage employees to propose and pilot new ideas using GenAI, building innovation from within PwC+1.
- Streamline Administrative Processes: Reduce regulatory burdens and enhance digital infrastructure to support entrepreneurial activity, particularly in traditionally bureaucratic environments Walton Family Foundation+4McKinsey & Company+4GEM Global Entrepreneurship Monitor+4.
Phase II (2027–2028): Ecosystem Building and Acceleration
- Institutional and University Integration: Expand startup labs, technology transfer, and spin-off support—like ambient education embedded in daily work On Digital Strategy | Dion Hinchcliffe.
- Scale Social and Inclusive Ventures: Support social enterprises as engines of inclusive innovation—currently some 10 million globally—especially focused on climate, digital inclusion, and marginalized groups World Economic Forum.
- Vertical Ecosystems Launch: Roll out ecosystem platforms around customer-centric needs (e.g., home, health, mobility), following the McKinsey model McKinsey & Company.
Phase III (2029–2030): Full Ecosystem Realization
- Ecosystem Interconnection: Link vertical platforms to co-create value across domains, enabling seamless customer and producer journeys within the ecosystemed economy.
- Robust Innovation Networks: Establish permanent structures—corporate venture units, public‑private partnerships, innovation hubs—to sustain entrepreneurship.
- Maximize Economic and Social Impact: Unlock the projected value pool of €2.3 trillion+ and enhance job creation, innovation, and resilience McKinsey & Company.
4. What Success Looks Like by 2030
- Diverse, Fluid Workforce: Modern organizations become talent hubs with employees, entrepreneurs, gig contributors, and partners interchangeable depending on needs.
- Digital and Educational Infrastructure: Ambient learning becomes the norm; employees (and aspiring entrepreneurs) upskill in real time On Digital Strategy | Dion Hinchcliffe+1.
- High Ecosystem Density and Interoperability: Multiple ecosystem platforms (vertical and regional) interact, enabling collaboration and innovation across boundaries.
- Inclusive Growth: Social enterprises are mainstream, driving green and digital inclusion; women and underrepresented groups successfully launch and scale ventures World Economic Forum.
- Economic Scale: Ecosystems generate tens of trillions in revenue, capturing substantial profits and delivering major societal value McKinsey & Company.
5. Summary Table: Transformation Milestones
| Phase | Key Focus | Indicators of Success |
|---|---|---|
| 2025–2026 | Hybrid models, citizen innovation, digital HR | Adoption of internal innovation loops, reduced bureaucracy |
| 2027–2028 | Ecosystem infrastructure, inclusive entrepreneurship | Launch of vertical platforms, rise of social ventures |
| 2029–2030 | Interconnected ecosystems, full integration | Sector-wide platforms, measurable economic gains and job growth |
Here are several real‑world case studies and best practices illustrating how various regions and initiatives have successfully transformed from traditional setups into thriving entrepreneurial ecosystems. These examples showcase strategies from grassroots innovation and digital inclusion to university‑anchored transformation and government‑driven incubation.
Case Studies & Learned Best Practices
1. eSamudaay – Community-Owned, Rural E-commerce Ecosystem (India)
- Summary: In Udupi, India, eSamudaay is a start‑up co‑founded by Anup Pai and Ravi Haldipur that crafts digital commons-based ecommerce ecosystems empowering micro‑entrepreneurs—from vegetable vendors to pharmacies—with a “business‑in‑a‑box” toolkit.
- Standout Practices:
- Open‑source, interoperable tech (like Beckn) ensures local data sovereignty and lower barriers to entry.
- Subscription model allows communities to own and govern the platform—unlike commission‑driven giants.
- Integration with public digital infrastructure (ONDC, India Stack) unlocks credit access via UPI transaction trails.
- As of early 2025, it expanded to eight towns with over 2,500 micro-entrepreneurs and substantial economic activity.
- Challenges: Scaling sustainably amid rising data costs, maintaining digital commons, and sustaining engagement.
OECD+3SpringerLink+3Wiley Online Library+3Financial Times
2. Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) – India’s National Ecosystem Builder
- Overview: Launched in 2016 under NITI Aayog, AIM is India’s flagship innovation ecosystem initiative.
- Key Programs:
- Atal Tinkering Labs (ATLs): Over 10,000 labs in schools across 722 districts by 2025, reaching more than 11 million students, fostering early innovation mindsets.
- Atal Incubation Centres (AICs): 72 operational incubation centres supporting over 3,500 startups and creating 32,000+ jobs by 2025. Notably, over 1,000 of these startups are led by women.
Wikipedia
3. University-Anchored Ecosystems & Civic Integration
- Muscle Shoals (Alabama, USA): A regional transformation driven by theory‑based ecosystem development:
- Focus on civic recognition of local talent, robust support networks, campus‑university anchoring, and creating a connected place for interaction.
- In four years, the project launched 30+ initiatives, boosted student entrepreneurial engagement, and raised over $1 million.
University of North Alabama+1
- Appalachian Region (USA):
- Ecosystem-building across varied contexts (Athens, OH; Chattanooga, WV), using strategies like philanthropy, food systems linkage, and regional funding.
- Emphasized stakeholder interviews, data-driven region-specific design, and site visits to tailor approaches.
Appalachian Regional Commission+1
- UAE Entrepreneurial Framework:
- Structured a unique ecosystem model anchored in Triple Helix (government, industry, academia).
- Aligned with UAE’s National Innovation Strategy and Abu Dhabi Economic Vision 2030, balancing gaps and opportunities to enhance support infrastructure.
Allied Business Academies
4. OECD Best Practice Benchmarks & Diagnostics
- The OECD offers comprehensive compendia of international ecosystem policies:
- Successful Models:
- Startup Delta / TechLeap.NL – Netherlands’ public‑private network knitting regional ecosystems.
- Startup Estonia – Government‑led ecosystem support.
- DutchCE – University‑based Centres for Entrepreneurship in the Netherlands.
- Diagnostics Tool (2025): First‑edition benchmarking to assess national entrepreneurial ecosystems and guide policy reinforcement.
OECD+1OECD
- Successful Models:
5. Academic Insights & Student Ecosystems
- Pasundan University (Indonesia):
- Ecosystem attributes (material, social, cultural) were surveyed among university students.
- Findings: Cultural factors exerted the strongest positive influence on fostering innovation.
ResearchGate
- AI‑Empowered Entrepreneurship Education (2025):
- Study proposes an AI scaffolding system to support personalized business plan development.
- Highlights the synergy of adaptive tech with human mentorship for more effective entrepreneurial education.
arXiv
Synthesis: Common Success Patterns
Across these case studies, key best practices emerge:
- Local Ownership & Digital Inclusion
- Build tools that empower local entrepreneurs (eSamudaay) with sovereignty, agency, and adaptability.
- Early Ecosystem Anchors
- Seed innovation at youth levels (ATLs, universities) to generate lifelong entrepreneurial cultures.
- Government-University-Industry Alignment
- Use frameworks like Triple Helix and national innovation strategies to coordinate ecosystem actors (UAE, AIM).
- Place-Based Design & Embedded Leadership
- Tailor to regional strengths, leverage civic leadership, and foster connected spaces (Muscle Shoals, Appalachia).
- Benchmarking & Policy Diagnostics
- Employ data-driven assessments to target ecosystem weak points and channel reinforcement effectively (OECD).
- Cultural & Social Dimensions
- Prioritize culture-building, fostering shared values, collaboration, and innovation mindset over just infrastructure.
- Tech-Enabled Learning & Inclusivity
- Integrate AI tools and mentorship to scale entrepreneurial skills (education models).
How This Informs 2025–2030 Transformation Strategy
- Localization with Scale: Initiatives like eSamudaay show the power of replicable, community-led models, anchored by inclusivity and modular tech.
- Structured National Initiatives: AIM exemplifies how coordinated, multi-layered systems—from school labs to incubators—can institutionalize entrepreneurship.
- Regional Tailoring & Universities as Catalysts: Anchored ecosystems drive localized innovation; universities and civic networks are key catalysts and connectors.
- Governance Alignment: National and regional policy strategies (OECD models, UAE’s framework) ensure coherence and resource flow across ecosystem actors.
- Data-Peak Strategy: Diagnostics (like OECD’s) help identify strengths and gaps, enabling adaptive, evidence-based policy interventions.
- Cultural First: Nurturing a strong innovation culture—through mentorship, shared values, peer learning—builds resilient ecosystems that outlast infrastructure.
Next Steps: Tailored Focus Options
Would you like to transfer your organisation from employee focused to entrepreneur driven in 2025? Explore one of these areas in more depth!
- Regional Implementation Guides – e.g., crafting local community ecosystems.
- Educational Ecosystem Playbook – leveraging schools, universities, and AI tools.
- Policy Framework Designs – aligning government, academia, and industry strategy.
- Performance Metrics & Diagnostics – designing measures like OECD’s approach
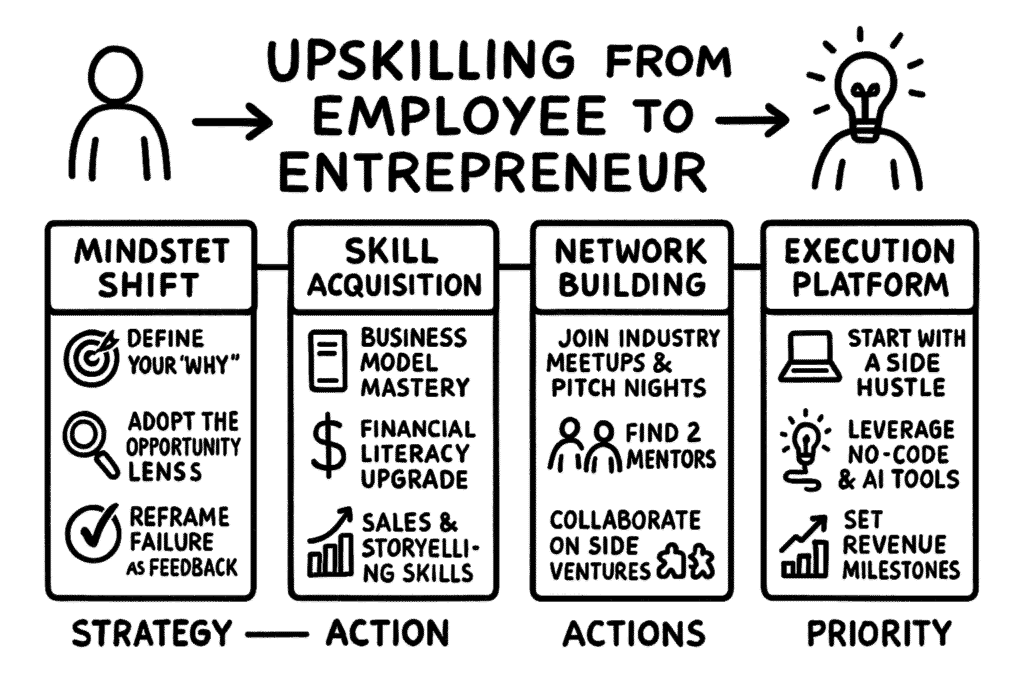
Upskilling from Employee to Entrepreneur: Key Strategies and Actions 2025
Here’s a clear, actionable 2025 roadmap for Upskilling from Employee to Entrepreneur, designed so a motivated professional can transition within months, not years.
I’ve structured it around four strategy pillars and twelve priority actions — practical, measurable, and directly tied to entrepreneurial success.
1️⃣ Strategy Pillar: Mindset Shift – From Task Taker to Value Creator
Goal: Rewire thinking from “doing my job” to “creating opportunities.”
Actions 2025:
- Define Your “Why” – Write down the problem you want to solve and why it matters.
Tool: Simon Sinek’s “Golden Circle” adapted for entrepreneurs. - Adopt the Opportunity Lens – Practice spotting inefficiencies and unmet needs in your current work/industry.
Habit: Record 3 ideas per week. - Reframe Failure as Feedback – Run small experiments (side projects, MVPs) and treat every setback as data.
2️⃣ Strategy Pillar: Skill Acquisition – Entrepreneurial Competence Stack
Goal: Acquire the core skills that bridge corporate experience and entrepreneurial action.
Actions 2025:
4. Business Model Mastery – Learn Lean Canvas and Osterwalder’s Business Model Canvas; apply to a simple test project.
5. Financial Literacy Upgrade – Master cash flow basics, profit margins, ROI, and break-even analysis.
6. Sales & Storytelling Skills – Practice pitching your idea in 60 seconds, then expand to a 5-minute investor version.
3️⃣ Strategy Pillar: Network Building – From Colleague Circles to Opportunity Ecosystem
Goal: Build an entrepreneurial support network before leaving your employee role.
Actions 2025:
7. Join Industry Meetups & Pitch Nights – Attend 1–2 per month; aim to speak or pitch at least once in 2025.
8. Find 2 Mentors – One from your industry, one from outside it, to challenge your assumptions.
9. Collaborate on Side Ventures – Co-create a micro-project with peers to test market response.
4️⃣ Strategy Pillar: Execution Platform – Build, Test, Launch
Goal: Turn skills + network into a functioning entrepreneurial venture.
Actions 2025:
10. Start with a Side Hustle – Low-capital, low-risk entry (digital product, consulting, marketplace).
11. Leverage No-Code & AI Tools – Use platforms like Bubble, Notion, ChatGPT to create MVPs in weeks.
12. Set Revenue Milestones – Aim for your first €1,000 from the side venture within 90 days.
Quick Transition Timeline 2025
| Quarter | Key Focus | Success Indicator |
|---|---|---|
| Q1 | Mindset & Core Skills | 1 completed MVP canvas + 2 skill certifications |
| Q2 | Network Activation | 2 mentors + 1 co-built side project |
| Q3 | Market Testing | MVP live, 10 paying customers |
| Q4 | Scaling & Transition Plan | Clear decision: full-time jump or parallel growth |
Success Metrics
- Skills: Can you explain your business model & value proposition in under 2 minutes?
- Network: Do you have 5+ people who’d introduce you to potential clients/investors tomorrow?
- Revenue: Have you proven customers will pay for your solution?