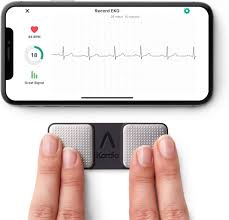
Problem Description
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) is a common heart condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterised by an irregular and often rapid heart rate that can increase the risk of strokes, heart failure, and other heart-related complications. The problem with AF is that it can go unnoticed because it doesn’t always cause noticeable symptoms. However, when symptoms do occur, they can be quite distressing and include palpitations, fatigue, shortness of breath, and dizziness.
Analysing Impact of AF on Your Health
The impact of AF on your health can be significant. It can lead to serious complications such as stroke and heart failure. A stroke occurs when the blood supply to part of your brain is interrupted or reduced, depriving brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients. This can lead to brain damage, disability or even death. Heart failure, on the other hand, doesn’t mean the heart has stopped working but that it’s not pumping blood as well as it should be. This can lead to fluid build-up in the lungs causing shortness of breath and swelling in the feet, ankles and legs.
Moreover, AF can also lead to additional heart rhythm problems. Rapid heart rates due to AF may cause a condition known as tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy. Over time, this condition weakens the heart muscle leading to symptoms of heart failure.
Finding Out the Main Root Cause of AF by Asking 5 Why Questions
1. Why does Atrial Fibrillation occur? AF occurs when the two upper chambers of the heart (the atria) beat irregularly and out of coordination with the two lower chambers (the ventricles). This irregular heartbeat is caused by abnormal electrical signals in the atria.
2. Why are there abnormal electrical signals in the atria? The abnormal electrical signals are often caused by damage to the heart’s electrical system from various conditions such as high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, heart attacks, or heart surgery.
3. Why do these conditions damage the heart’s electrical system? These conditions can cause changes in the heart muscle, leading to the development of areas with abnormal electrical activity. These areas can disrupt the normal flow of electrical signals through the heart, leading to AF.
4. Why do changes in the heart muscle lead to areas with abnormal electrical activity? Changes in the heart muscle can lead to scarring or thickening (fibrosis), which can disrupt the normal electrical pathways in the heart. This disruption can cause the electrical signals to become disorganised and rapid, leading to AF.
5. Why does fibrosis disrupt normal electrical pathways in the heart? Fibrosis creates physical barriers that can block or slow down the electrical signals as they travel through the heart. This can cause the signals to become disorganised and rapid, leading to AF.
Conclusion: Summarizing The Main Root Causes of Having AF
In conclusion, Atrial Fibrillation is a complex condition with multiple root causes. It primarily stems from abnormal electrical signals in the atria, which are often caused by damage to the heart’s electrical system from various conditions such as high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, heart attacks or heart surgery. These conditions can cause changes in the heart muscle, leading to fibrosis that disrupts normal electrical pathways and causes disorganised and rapid signals that result in AF. Understanding these root causes is crucial for effective prevention and treatment strategies for Atrial Fibrillation.