The Power of Precision Medicine: How Personalized Treatment is Changing Cancer Care
Precision medicine, also known as personalized medicine, is an innovative approach to cancer treatment that takes into account an individual’s unique genetic makeup, lifestyle, and environment. It aims to provide targeted therapies and interventions that are tailored to the specific needs of each patient. This approach has gained significant attention and recognition in recent years due to its potential to revolutionize cancer care.
The concept of precision medicine in cancer treatment has been around for several decades, but it has gained momentum in recent years with advancements in technology and our understanding of the human genome. The Human Genome Project, completed in 2003, played a crucial role in laying the foundation for precision medicine by mapping the entire human genome. This breakthrough allowed researchers and clinicians to identify genetic variations that contribute to the development and progression of cancer.
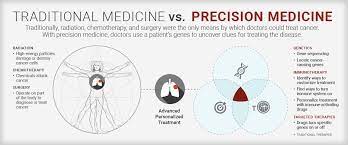
Precision medicine is of utmost importance in cancer care because it allows for more accurate diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment selection. By analyzing a patient’s genetic profile, doctors can identify specific mutations or alterations that are driving the growth of cancer cells. This information helps them choose targeted therapies that are more likely to be effective and avoid treatments that may be ineffective or cause unnecessary side effects. Precision medicine has the potential to improve patient outcomes, reduce healthcare costs, and ultimately save lives.
The Importance of Personalized Treatment in Cancer Care
Traditional cancer treatment methods, such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy, have been the standard of care for many years. While these treatments have been effective for some patients, they often come with significant limitations. One of the main limitations is that these treatments are not tailored to the individual characteristics of each patient. They are based on general guidelines and protocols that may not take into account the unique biology of each person’s cancer.
Personalized treatment, on the other hand, takes into account the specific genetic alterations or mutations present in a patient’s tumor. This allows doctors to choose treatments that target these specific alterations, increasing the likelihood of a positive response. Personalized treatment also takes into consideration other factors, such as a patient’s overall health, lifestyle, and preferences. This holistic approach to cancer care ensures that patients receive the most appropriate and effective treatments for their individual needs.
The benefits of personalized treatment in cancer care are numerous. Firstly, it can lead to improved treatment outcomes. By targeting the specific genetic alterations driving the growth of cancer cells, personalized treatments have the potential to be more effective than traditional treatments. This can result in better response rates, longer survival times, and improved quality of life for patients.
Another benefit of personalized treatment is the potential to reduce side effects. Traditional treatments often come with significant side effects that can be debilitating for patients. By using targeted therapies that specifically attack cancer cells while sparing healthy cells, personalized treatment can minimize the toxic effects on the body. This can lead to a better quality of life for patients during and after treatment.
Understanding the Role of Genomics in Precision Medicine
Genomics is the study of an individual’s entire genetic makeup, including all of their genes and their interactions with each other and the environment. In precision medicine, genomics plays a crucial role in understanding the underlying genetic changes that drive the development and progression of cancer.
Genomic testing involves analyzing a patient’s DNA to identify specific genetic alterations or mutations that are associated with cancer. This can be done through various techniques, such as next-generation sequencing or polymerase chain reaction (PCR). By analyzing the genetic profile of a tumor, doctors can identify specific mutations or alterations that are driving the growth of cancer cells.
Genomic testing is used in precision medicine to guide treatment decisions. By identifying specific genetic alterations, doctors can choose targeted therapies that are designed to attack these specific alterations. This approach has been particularly successful in certain types of cancer, such as lung cancer and melanoma, where specific mutations have been identified and targeted therapies have been developed.
Examples of genomic testing in cancer treatment include testing for mutations in the EGFR gene in lung cancer patients, which can help determine whether they are eligible for targeted therapies such as EGFR inhibitors. Another example is testing for mutations in the BRAF gene in melanoma patients, which can help guide treatment decisions and determine whether they are eligible for targeted therapies such as BRAF inhibitors.
Precision Medicine and Targeted Therapies for Cancer Treatment
Targeted therapies are a key component of precision medicine in cancer treatment. These therapies are designed to specifically target and attack cancer cells while sparing healthy cells, leading to more effective and less toxic treatments.
Targeted therapies work by targeting specific molecules or pathways that are involved in the growth and survival of cancer cells. They can be small molecules that inhibit specific proteins or antibodies that bind to specific receptors on cancer cells. By blocking these molecules or pathways, targeted therapies can disrupt the growth and survival of cancer cells, leading to tumor shrinkage and improved patient outcomes.
There are several examples of targeted therapies that have been developed for different types of cancer. In breast cancer, for example, targeted therapies such as trastuzumab (Herceptin) and pertuzumab (Perjeta) target the HER2 protein, which is overexpressed in some breast cancers. These therapies have been shown to improve survival rates in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer.
In lung cancer, targeted therapies such as gefitinib (Iressa) and erlotinib (Tarceva) target mutations in the EGFR gene, which are present in a subset of lung cancer patients. These therapies have been shown to be highly effective in patients with EGFR-mutated lung cancer, leading to improved response rates and longer survival times.
The Advantages of Precision Medicine in Cancer Care
Precision medicine offers several advantages over traditional cancer treatment methods. Firstly, it can lead to improved treatment outcomes. By targeting the specific genetic alterations driving the growth of cancer cells, precision medicine allows for more effective treatments that are tailored to the individual needs of each patient. This can result in better response rates, longer survival times, and improved quality of life for patients.
Another advantage of precision medicine is the potential to reduce side effects. Traditional treatments such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy often come with significant side effects that can be debilitating for patients. By using targeted therapies that specifically attack cancer cells while sparing healthy cells, precision medicine can minimize the toxic effects on the body. This can lead to a better quality of life for patients during and after treatment.
Precision medicine also has the potential to improve the overall quality of care for cancer patients. By taking into account a patient’s unique genetic makeup, lifestyle, and environment, doctors can provide personalized treatment plans that are tailored to their individual needs. This holistic approach to cancer care ensures that patients receive the most appropriate and effective treatments, leading to better outcomes and improved patient satisfaction.
Challenges and Limitations of Precision Medicine in Cancer Treatment
While precision medicine holds great promise in cancer care, there are several challenges and limitations that need to be addressed. One of the main challenges is limited access to genomic testing. Genomic testing is still relatively expensive and not widely available in many healthcare settings. This limits the ability of doctors to identify specific genetic alterations in their patients and choose targeted therapies accordingly.
The high cost of precision medicine is another significant limitation. Genomic testing can be expensive, especially when multiple tests are required to identify specific genetic alterations. In addition, targeted therapies can also be costly, with some drugs costing tens of thousands of dollars per month. This raises concerns about the affordability and accessibility of precision medicine for all patients, regardless of their socioeconomic status.
Another challenge is the lack of standardization in precision medicine. While there have been significant advancements in genomic testing and targeted therapies, there is still a lack of consensus on best practices and guidelines. This can lead to variability in the use of precision medicine and inconsistencies in treatment decisions. Standardization is crucial to ensure that all patients receive the same level of care and have equal access to precision medicine.
The Future of Precision Medicine in Cancer Care
Despite the challenges and limitations, the future of precision medicine in cancer care looks promising. There are several advancements and developments on the horizon that have the potential to further revolutionize cancer treatment.
One of the key advancements is in genomic testing. As technology continues to improve, genomic testing is becoming more affordable and accessible. Next-generation sequencing, for example, has significantly reduced the cost and time required for genomic testing, making it more feasible for routine clinical use. This will allow more patients to benefit from precision medicine and receive targeted therapies based on their specific genetic alterations.
Another area of advancement is the development of new targeted therapies. Researchers are constantly discovering new molecular targets and developing drugs that can specifically target these targets. This will expand the range of targeted therapies available for different types of cancer and increase the likelihood of finding effective treatments for individual patients.
Furthermore, there is a growing recognition of the importance of integrating precision medicine into standard cancer care. Precision medicine is no longer seen as a separate approach, but rather as an integral part of cancer treatment. This integration will ensure that all patients have equal access to precision medicine and receive the most appropriate and effective treatments for their individual needs.
Case Studies: Success Stories of Precision Medicine in Cancer Treatment
There are numerous success stories of precision medicine in cancer treatment that highlight its potential to improve patient outcomes and save lives. One such success story is that of Emily Whitehead, a young girl who was diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) at the age of five. Despite undergoing traditional chemotherapy treatments, her cancer relapsed multiple times.
Emily’s doctors decided to try a new experimental treatment called CAR-T cell therapy, which is a form of precision medicine. This therapy involves modifying a patient’s own immune cells to recognize and attack cancer cells. Emily became the first pediatric patient to receive CAR-T cell therapy and experienced a complete remission. Today, she is cancer-free and living a normal, healthy life.
Another success story is that of Jimmy Carter, the former President of the United States. In 2015, Carter was diagnosed with metastatic melanoma that had spread to his brain and liver. He underwent surgery and radiation therapy, but his cancer continued to progress. His doctors decided to try a targeted therapy called pembrolizumab (Keytruda), which targets a protein called PD-1 that is involved in suppressing the immune system’s response to cancer cells.
Carter responded well to the treatment and experienced a complete remission. He has since become an advocate for precision medicine and has been vocal about the importance of early detection and access to innovative treatments.
These success stories highlight the potential of precision medicine to transform cancer care and provide hope for patients who have exhausted traditional treatment options. They also emphasize the importance of continued research and development in precision medicine to further improve patient outcomes and save lives.
Ethical and Legal Implications of Precision Medicine in Cancer Care
While precision medicine offers great promise in cancer care, it also raises several ethical and legal implications that need to be addressed. One of the main concerns is privacy. Genomic testing involves analyzing a patient’s DNA, which contains highly personal and sensitive information. There are concerns about how this information is stored, shared, and protected from unauthorized access.
Informed consent is another important ethical consideration in precision medicine. Patients need to be fully informed about the risks, benefits, and limitations of genomic testing and targeted therapies before making decisions about their treatment. This requires clear and transparent communication between doctors and patients, as well as the provision of accurate and up-to-date information.
Access to precision medicine is also an ethical concern. While precision medicine has the potential to improve patient outcomes, it is important to ensure that all patients have equal access to these innovative treatments. This requires addressing issues of affordability, insurance coverage, and disparities in healthcare access.
The Cost of Precision Medicine in Cancer Treatment
One of the main challenges of precision medicine in cancer treatment is the high cost associated with genomic testing and targeted therapies. Genomic testing can be expensive, especially when multiple tests are required to identify specific genetic alterations. The cost of targeted therapies can also be significant, with some drugs costing tens of thousands of dollars per month.
The high cost of genomic testing is due to several factors, including the complexity of the technology, the need for specialized equipment and expertise, and the cost of analyzing and interpreting the data. As technology continues to improve and become more efficient, the cost of genomic testing is expected to decrease. However, it is still a significant barrier for many patients and healthcare systems.
The cost of targeted therapies is also a concern. These therapies are often priced based on their perceived value and the potential benefits they offer to patients. However, this can lead to high prices that are not affordable for many patients, especially those without insurance coverage or with limited financial resources.
Insurance coverage for precision medicine is another important consideration. While some insurance companies cover the cost of genomic testing and targeted therapies, others may not. This can create disparities in access to precision medicine and limit its potential impact on patient outcomes.
The Impact of Precision Medicine on Cancer Care and Patients’ Lives
Precision medicine has the potential to revolutionize cancer care by providing personalized treatments that are tailored to the individual needs of each patient. By analyzing a patient’s genetic profile, doctors can identify specific genetic alterations or mutations that are driving the growth of cancer cells. This information helps them choose targeted therapies that are more likely to be effective and avoid treatments that may be ineffective or cause unnecessary side effects.
The advantages of precision medicine in cancer care are numerous. It can lead to improved treatment outcomes, reduced side effects, and a better quality of life for patients. However, there are also challenges and limitations that need to be addressed, such as limited access to genomic testing, high cost, and lack of standardization.
The future of precision medicine in cancer care looks promising, with advancements in genomic testing, the development of new targeted therapies, and the integration of precision medicine into standard cancer care. Continued research and development in precision medicine is crucial to further improve patient outcomes and save lives.
Overall, precision medicine has the potential to transform cancer care and improve the lives of millions of patients worldwide. It offers hope for more effective treatments, reduced side effects, and better quality of life. With continued advancements and investment in precision medicine, we can look forward to a future where cancer is no longer a devastating disease but a manageable condition.