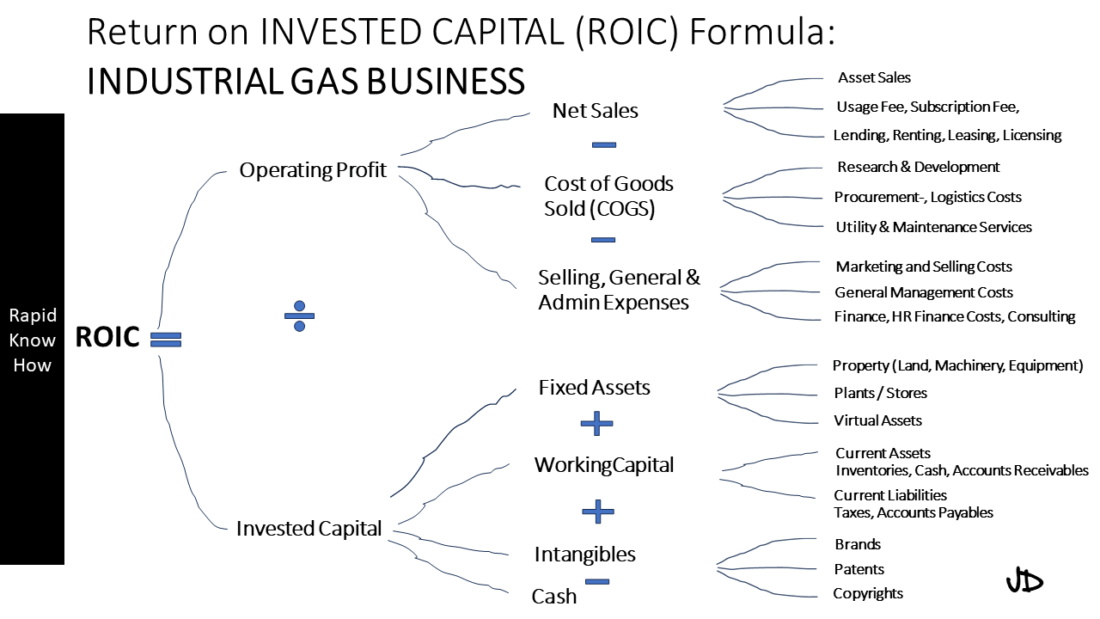
Return on Invested Capital (ROIC) is a crucial financial metric that measures how effectively a company generates profits from its capital investments. It is particularly relevant in capital-intensive industries such as industrial gases, where companies must make significant investments in plant, equipment, and technology to produce and distribute their products.
In the industrial gases sector, cracking the ROIC code involves several key elements: operations efficiency levers, management strategic investments, optimal capital structure, and managing taxes efficiently. Let’s delve into each of these aspects.
1. Operations Efficiency Levers
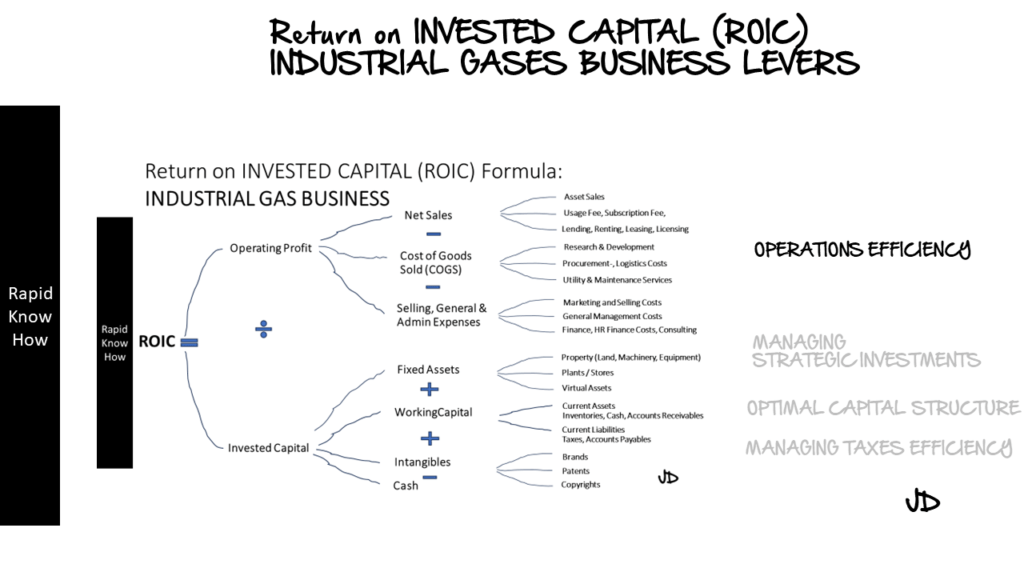
Operational efficiency is paramount in the industrial gases industry. Companies must strive to maximise output while minimising input costs. This can be achieved through various levers such as process optimisation, energy efficiency, waste reduction, and supply chain management.
Process optimisation involves streamlining production processes to reduce waste and improve productivity. This could involve investing in advanced technologies or implementing lean manufacturing principles.
Energy efficiency is another critical lever. Industrial gas production is energy-intensive, so any improvements in energy efficiency can significantly reduce costs and improve ROIC.
Waste reduction is also essential. By reducing waste, companies can lower costs and improve environmental performance – a growing concern for many stakeholders.
Finally, effective supply chain management can help reduce costs and improve service levels. This might involve optimising logistics processes or building strategic partnerships with suppliers.
2. Management Strategic Investments Lever
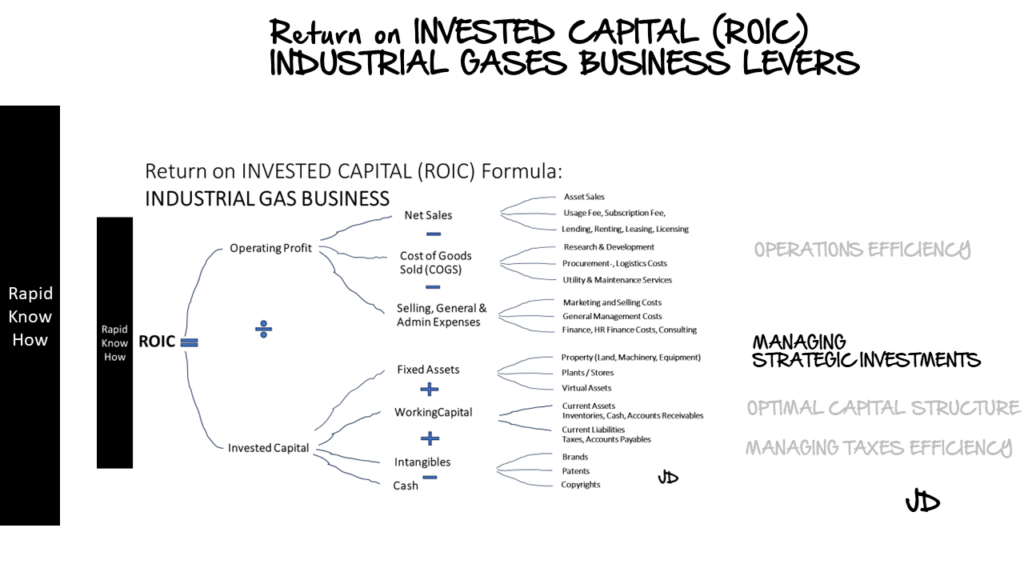
Strategic investments are crucial for driving growth and improving ROIC in the industrial gases industry. These might include investing in new production facilities, expanding into new markets, or developing innovative products and services.
When making strategic investments, management must carefully consider the potential return on investment (ROIC). This involves assessing the potential revenue growth, cost savings, and other benefits that the investment could deliver by tools as business cases and sensitivity analysis.
3. Optimal Capital Structure Lever
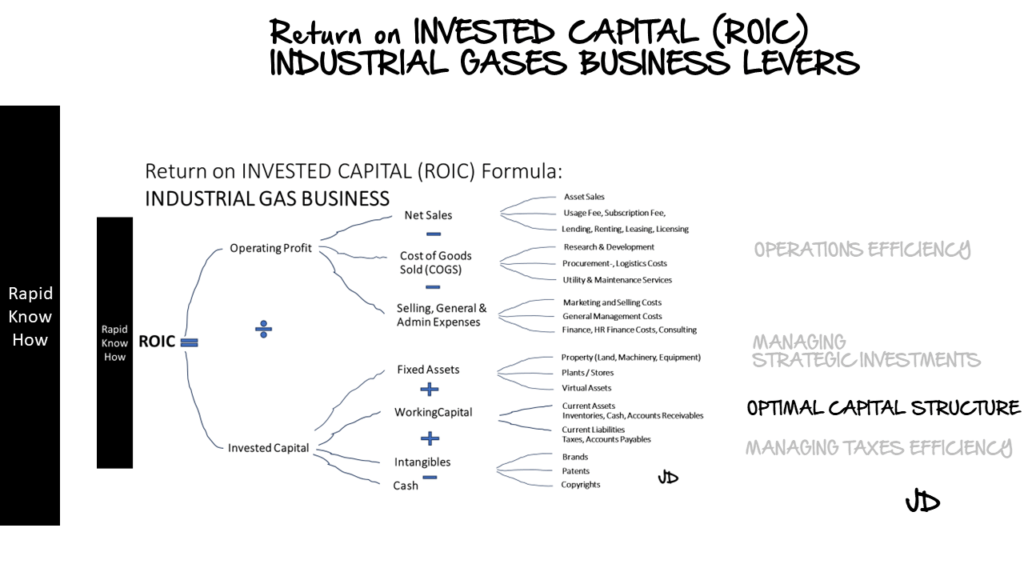
The optimal capital structure is the mix of debt and equity that minimises a company’s cost of capital and maximises its ROIC. In the industrial gases industry, companies often need to borrow large sums of money to finance their capital-intensive operations. However, too much debt can increase financial risk and potentially reduce ROIC.
Therefore, companies must carefully manage their capital structure to balance the benefits of debt (such as tax deductibility) against the risks (such as financial distress). This might involve using a mix of debt and equity financing, or it might involve using more complex financial instruments such as convertible bonds or derivatives.
4. Managing Taxes Efficiently Lever
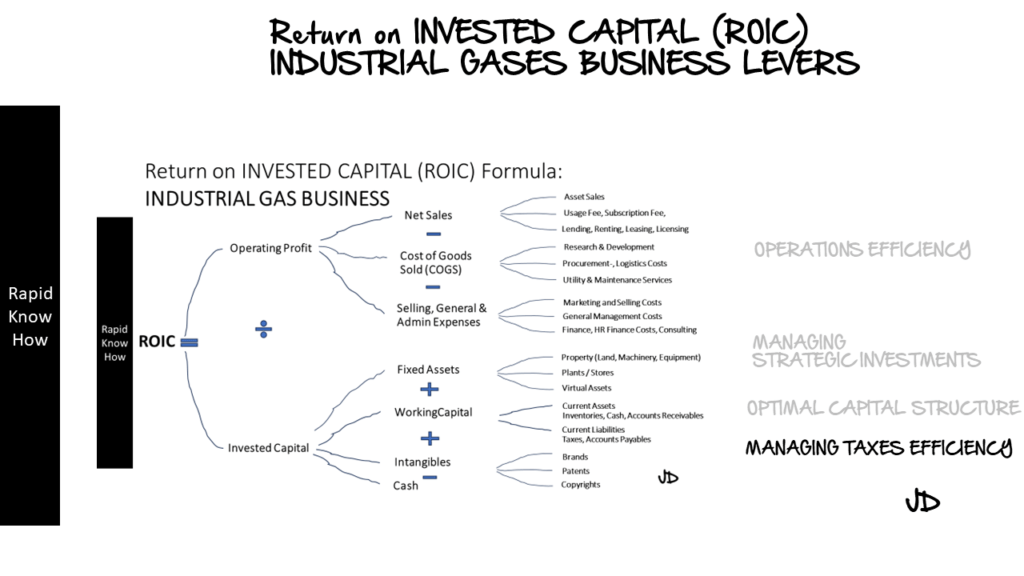
Finally, managing taxes efficiently is crucial for improving ROIC. This involves not only minimising tax liabilities but also taking advantage of tax incentives and credits.
For example, many countries offer tax incentives for companies that invest in research and development (R&D), energy efficiency, or other strategic areas. By taking advantage of these incentives, companies can reduce their tax liabilities and improve their ROIC.
In conclusion, cracking the ROIC code in the industrial gases industry involves a combination of operational efficiency, strategic investments, optimal capital structure, and efficient tax management. By focusing on these areas, companies can improve their financial performance and create value for their shareholders.