Market sizing is a crucial aspect of strategic planning for any business, and it’s no different for the industrial gas market. Understanding the size and value of both the served and potential market can help businesses make informed decisions about their growth strategies, product development, and marketing efforts.
To assess the size and value of the served and potential industrial gas market, we need to analyze both the demand side and the supply side.
Analysing the Demand Side of the Industrial Gas Market
On the demand side, we need to understand who the customers are, what their needs are, how many of them there are, and how these factors might change over time. This involves looking at various factors such as industry trends, economic indicators, demographic data, and technological advancements. For instance, if there’s a growing trend in industries that heavily rely on industrial gases like healthcare or food processing, this could indicate an increase in demand for industrial gases.
In addition to understanding current demand, it’s also important to forecast future demand. This can be done by analyzing trends in related markets or industries, as well as considering broader economic or societal trends that could impact demand.
Analysing the Supply Side of the Industrial Gas Market
On the supply side, we need to understand who the suppliers are, what their capacities are, what their cost structures look like, and how these factors might change over time. This involves looking at things like production capacity, cost of raw materials, labor costs, and technological advancements in production methods.
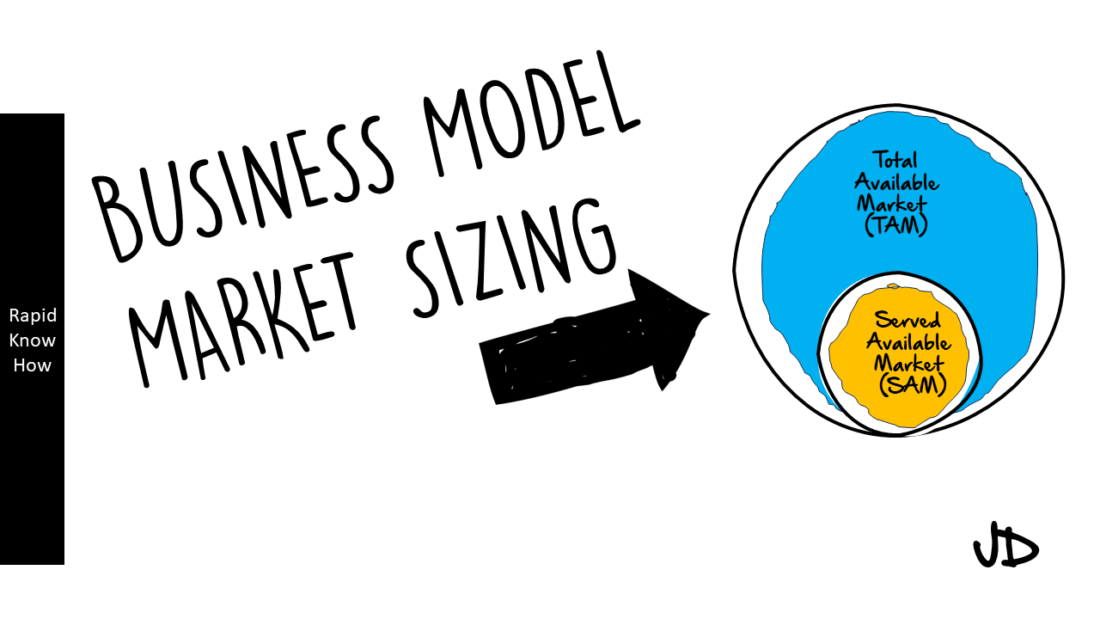
Market Sizing the Industrial Gas Market
Comparing the Total Available Industrial Gas Market (TAIGM) with the Served Available Industrial Gas Market (SEM) can provide valuable insights into market penetration and potential growth opportunities.
The TAIGM refers to all potential customers who could potentially use industrial gases. This includes not only current users but also those who might use industrial gases if certain conditions were met (for example if prices were lower or if there were more suppliers).
The SEM on the other hand refers to current users of industrial gases. These are customers who are currently being served by existing suppliers.
By comparing TAIGM with SEM we can get a sense of how much of the potential market is currently being served. If SEM is significantly smaller than TAIGM this could indicate that there is a large untapped market that could be targeted for growth.
However, it’s important to note that just because there is a large potential market doesn’t necessarily mean that it’s easy or profitable to serve. There may be barriers to entry such as high capital costs or regulatory hurdles that make it difficult for new suppliers to enter the market.
In conclusion, assessing the size and value of both the served and potential industrial gas market involves a detailed analysis of both demand-side and supply-side factors. Comparing TAIGM with SEM can provide valuable insights into market penetration and potential growth opportunities. However, it’s also important to consider any barriers to entry that might make it difficult for new suppliers to serve this potential market.