Industrial gases are a critical component in a wide range of industries, from healthcare to manufacturing, food processing to energy production. These gases, which include oxygen, nitrogen, argon, helium, and carbon dioxide, among others, are stored and transported in high-pressure cylinders. Managing these cylinders effectively is crucial for safety, efficiency, and cost control. This is where the concept of CYLINDER CONTROL comes into play.
Needs:
The need for effective CYLINDER CONTROL in the industrial gases sector cannot be overstated. The primary needs can be categorized into three main areas: safety, efficiency, and cost control.
Safety: Industrial gases can be hazardous if not handled correctly. They are often stored under high pressure and can cause serious harm if there’s a leak or explosion. Therefore, it’s essential to have a robust system for monitoring and controlling the storage and transportation of these cylinders.
Efficiency: In industries where time is money, the efficient management of gas cylinders can significantly impact productivity. This includes knowing where each cylinder is located at any given time, how much gas is left in each cylinder, when they need to be refilled or replaced.
Cost Control: Mismanagement of cylinders can lead to unnecessary costs. This could be due to lost or stolen cylinders, wasted gas due to leaks or inefficient usage, or fines for non-compliance with safety regulations.
Solution:
The solution lies in implementing a comprehensive CYLINDER CONTROL system that addresses all these needs. Such a system would include several components:
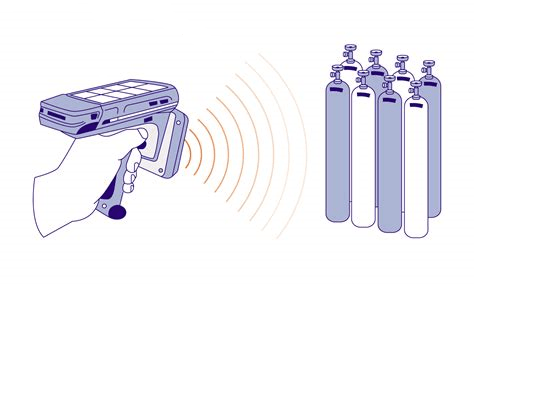
1. Tracking System: This could involve RFID tags or barcodes on each cylinder that allow it to be tracked throughout its lifecycle – from filling to delivery to return.
2. Monitoring System: Sensors on each cylinder could monitor pressure levels and alert operators if there’s a leak or if the gas level is getting low.
3. Compliance System: A system that ensures all safety regulations are being followed, including proper storage and handling procedures.
4. Reporting System: A system that provides detailed reports on cylinder usage, location, and status, allowing for better decision-making and cost control.
Action:
Implementing a CYLINDER CONTROL system involves several steps:
1. Assessment: The first step is to assess your current cylinder management practices and identify areas for improvement.
2. Selection: Next, you need to select a CYLINDER CONTROL system that fits your needs. This could involve researching different vendors, comparing features and prices, and possibly conducting a pilot test.
3. Implementation: Once you’ve selected a system, the next step is implementation. This will likely involve training staff on the new system and possibly some changes to your existing processes.
4. Review: After the system has been in place for a while, it’s important to review its effectiveness and make any necessary adjustments.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, cracking the CYLINDER CONTROL code is all about understanding your needs in terms of safety, efficiency, and cost control, then implementing a system that meets those needs. It’s not necessarily an easy task, but with careful planning and execution, it can lead to significant improvements in how you manage your industrial gases.