Question: How Can We Effectively Classify Heart Attack Patients Utilising Key Criteria Such as Blood Pressure, Oxygen Respiration, and Heart Rhythm?
In the realm of medical science, the classification of heart attack patients is a critical task that requires meticulous attention to detail and a comprehensive understanding of various physiological parameters. The process involves the careful examination of several key criteria, including blood pressure, oxygen respiration, and heart rhythm. These factors play a pivotal role in determining the severity of a patient’s condition and subsequently guiding the course of treatment.

Blood pressure is one of the most crucial indicators of cardiovascular health. A consistent reading of high blood pressure (hypertension) can potentially lead to severe heart complications, including heart attacks. Therefore, monitoring a patient’s blood pressure levels can provide valuable insights into their risk of suffering a heart attack

Oxygen respiration, or the rate at which oxygen is inhaled and carbon dioxide is exhaled, is another vital criterion. When the body doesn’t receive an adequate supply of oxygen due to impaired respiratory function, it can put undue strain on the heart, increasing the likelihood of a heart attack. Hence, assessing a patient’s oxygen respiration rate can help in identifying potential risks and implementing preventive measures.
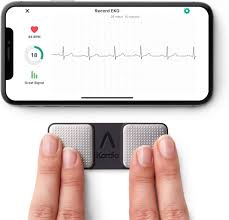
The third key criterion is heart rhythm. Irregularities in heart rhythm, or arrhythmias, can disrupt the normal functioning of the heart and may lead to a heart attack if left untreated. By closely monitoring a patient’s heart rhythm using electrocardiograms (ECGs), healthcare professionals can detect any abnormalities early on and take appropriate action.
In conclusion, classifying heart attack patients involves an intricate process that relies heavily on these three critical criteria: blood pressure, oxygen respiration, and heart rhythm. By accurately measuring these factors and interpreting their implications, medical professionals can effectively classify patients according to their risk level and provide them with the most suitable treatment options. This not only aids in managing the patient’s current condition but also plays a significant role in preventing future heart-related complications.