The business designing sector is also experiencing significant innovation driven by advancements in technology, changing consumer preferences, and the need for sustainable and user-centric solutions. Here are some key areas of innovation in the designing sector:
1. Digital Design Tools: The advent of digital design tools has revolutionized the way designers work. Software applications such as computer-aided design (CAD), 3D modeling, and virtual reality (VR) tools enable designers to create and visualize designs in a more efficient and realistic manner. These tools enhance the speed, accuracy, and creativity of the design process.
2. User-Centric Design: Designers are increasingly focusing on creating user-centric solutions that prioritize the needs and preferences of the end-users. User research, usability testing, and design thinking methodologies are being employed to understand user behaviors, pain points, and aspirations. This approach ensures that designs are intuitive, accessible, and provide a seamless user experience.
3. Sustainable Design: With growing concerns about environmental impact, designers are incorporating sustainability principles into their work. Sustainable design aims to minimize resource consumption, reduce waste, and create products and services that have a positive environmental impact. This includes using eco-friendly materials, designing for recyclability, and promoting circular economy principles.
4. Design for Social Impact: Designers are increasingly using their skills to address social challenges and create positive change. Design for social impact involves developing solutions that address social issues such as poverty, inequality, healthcare, and education. This includes designing inclusive products, services, and environments that improve the quality of life for marginalized communities.
5. Collaborative Design: Designers are embracing collaborative approaches to problem-solving. They are working in multidisciplinary teams that include experts from various fields such as engineering, marketing, psychology, and business. This collaborative design process fosters innovation, diversity of perspectives, and holistic solutions.
6. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR technologies are being used to enhance the design process and create immersive experiences. Designers can use AR and VR to visualize and test designs in real-world contexts, allowing for better evaluation and refinement. These technologies also enable clients and users to experience and interact with designs before they are implemented.
7. Design Automation: Automation technologies are being integrated into the design process to streamline repetitive tasks and increase efficiency. Design automation tools can generate design variations, perform simulations, and optimize designs based on predefined criteria. This allows designers to focus on more creative and strategic aspects of the design process.
8. Biodesign: Biodesign involves using biological systems and processes as inspiration for design solutions. Designers are exploring biomimicry, where they study nature’s designs and apply those principles to create sustainable and efficient solutions. Biodesign can lead to innovations in areas such as architecture, product design, and urban planning.
9. Emotional Design: Emotional design focuses on creating products and experiences that evoke positive emotions and connect with users on a deeper level. Designers are incorporating elements such as aesthetics, storytelling, and sensory experiences to create emotionally engaging designs. This approach enhances user satisfaction, brand loyalty, and overall product success.
10. Continuous Learning and Skill Development: Designers are investing in continuous learning and skill development to stay updated with the latest design trends, technologies, and methodologies. They attend workshops, conferences, and online courses to expand their knowledge and enhance their design capabilities. Continuous learning ensures that designers can deliver innovative and impactful solutions to clients.
These innovations in the designing sector are reshaping the way designers approach their work, collaborate with others, and create solutions that meet the evolving needs of users and society. By embracing these innovations, designers can drive positive change, create sustainable solutions, and enhance the overall user experience.
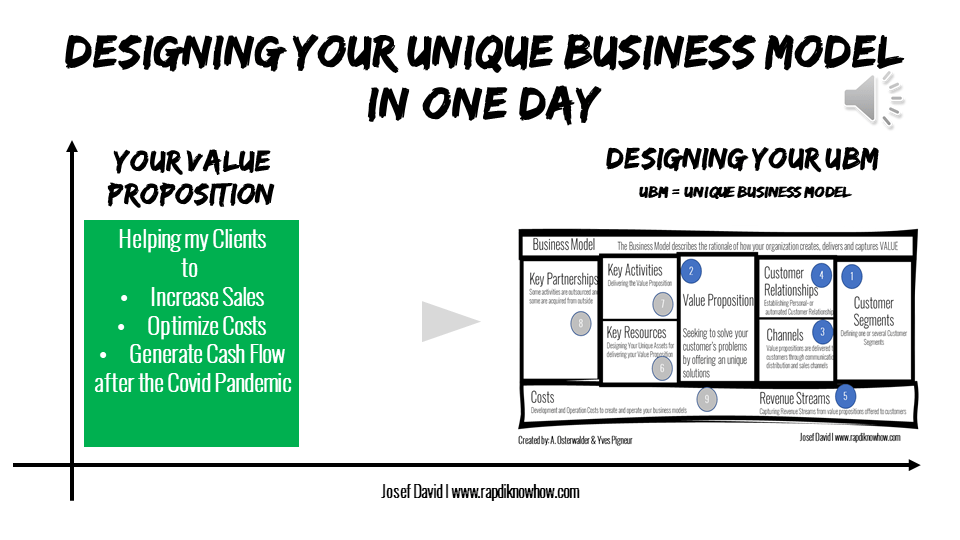
Understanding the INNOVATION of the BUSINESS MODEL DESIGNING THINKING
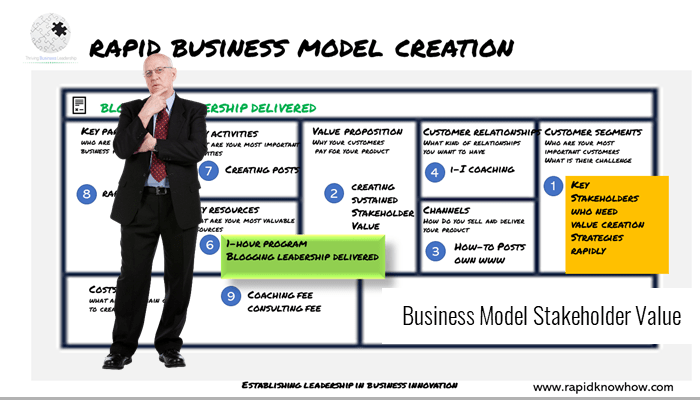
The business model designing sector is also experiencing significant innovation as companies seek to create new and sustainable ways of generating value and staying competitive. Here are some key areas of innovation in the business model designing sector:
1. Platform Business Models: Platform business models have gained popularity in recent years, driven by advancements in technology and changing consumer behaviors. These models involve creating a digital platform that connects multiple stakeholders, such as buyers and sellers, and facilitates transactions or interactions. Platforms like Airbnb, Uber, and Amazon have disrupted traditional industries and created new opportunities for value creation.
2. Subscription and Membership Models: Subscription and membership models have become increasingly popular across various industries. Instead of selling products or services on a one-time basis, companies offer ongoing access or benefits in exchange for a recurring fee. This model provides a predictable revenue stream and fosters customer loyalty. Examples include Netflix, Spotify, and Amazon Prime.
3. Freemium Models: Freemium models offer a basic version of a product or service for free, while charging for premium features or additional functionality. This model allows companies to attract a large user base and monetize through upselling or offering premium upgrades. Companies like Dropbox and LinkedIn have successfully implemented freemium models.
4. Sharing Economy Models: The sharing economy has disrupted traditional industries by enabling individuals to share or rent out their underutilized assets, such as homes, cars, or skills. Companies like Airbnb, Uber, and TaskRabbit have created platforms that connect individuals who have something to share with those who need it, creating new revenue streams and opportunities for value creation.
5. Ecosystem Business Models: Ecosystem business models involve creating an interconnected network of companies, customers, and other stakeholders that collaborate and share resources to create value. These models leverage the strengths and capabilities of multiple partners to deliver comprehensive solutions to customers. Examples include Apple’s ecosystem of devices, apps, and services, and Alibaba’s ecosystem of e-commerce, logistics, and financial services.
6. Data-driven Business Models: With the proliferation of data and advancements in analytics, companies are leveraging data to create new business models. Data-driven business models involve collecting, analyzing, and monetizing data to provide personalized products, services, or insights. Companies like Google, Facebook, and Amazon have built their business models around data-driven strategies.
7. Circular Economy Models: Circular economy models aim to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency by designing products and services that can be reused, repaired, or recycled. These models focus on creating closed-loop systems where materials and resources are continuously cycled back into the production process. Companies like Patagonia and Interface have embraced circular economy principles in their business models.
8. Social Enterprise Models: Social enterprise models combine business objectives with a social or environmental mission. These models aim to create positive social impact while generating sustainable revenue. Social enterprises often reinvest their profits into their mission or use innovative financing models to support their social goals. Examples include TOMS Shoes and Grameen Bank.
9. Agile and Lean Startup Models: Agile and lean startup models emphasize rapid experimentation, iterative development, and customer feedback to quickly validate business ideas and adapt to market needs. These models enable companies to minimize risks, optimize resources, and accelerate innovation. Companies like Spotify and Zappos have embraced agile and lean startup methodologies in their business models.
10. Co-creation and Open Innovation Models: Co-creation and open innovation models involve collaborating with external stakeholders, such as customers, suppliers, or even competitors, to jointly develop new products, services, or business models. These models leverage the collective intelligence and expertise of a broader ecosystem to drive innovation and create value. Examples include LEGO’s Ideas platform and Procter & Gamble’s Connect + Develop program.
These innovations in the business model designing sector are reshaping the way companies create, deliver, and capture value. By embracing these innovations, companies can stay competitive, adapt to changing market dynamics, and create sustainable business models that meet the evolving needs of customers and society.