Return on Invested Capital (ROIC) is a crucial financial metric that investors use to gauge a company’s profitability and efficiency. It measures how effectively a company uses its capital to generate profits. The higher the ROIC, the more efficiently a company is using its capital to create wealth for shareholders.
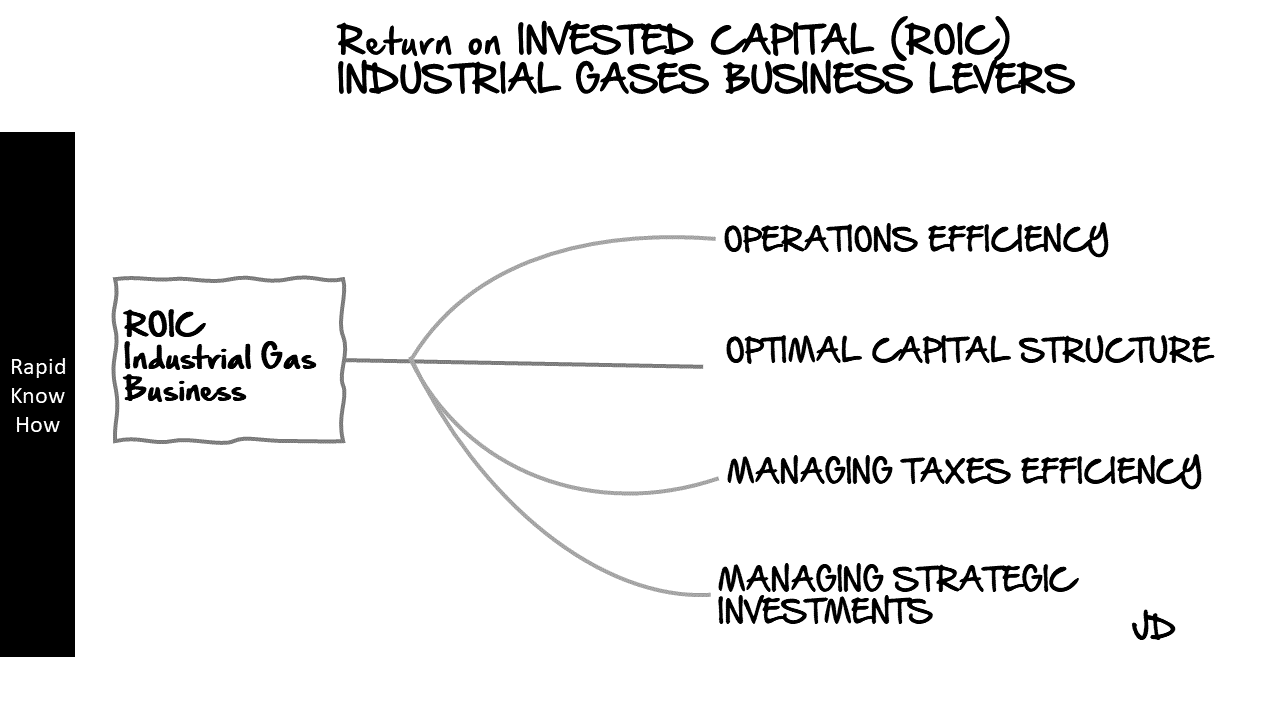
There are several levers that can impact ROIC, including operational efficiency, capital structure, tax efficiency, and strategic investments. Let’s delve into each of these levers in detail:
1. Operational Efficiency: This refers to how well a company uses its resources to produce goods or services. Companies with high operational efficiency can produce more output with the same amount of input, leading to higher profits and thus a higher ROIC.
2. Capital Structure: This refers to how a company finances its operations and growth using different sources of funds, such as debt and equity. A company with an optimal capital structure can minimize its cost of capital and maximize its ROIC.
3. Tax Efficiency: This refers to how well a company manages its tax obligations. Companies that are able to minimize their tax liabilities through legal means can retain more of their earnings, leading to a higher ROIC.
4. Strategic Investments: These are investments made by a company in new projects or businesses that have the potential to generate high returns in the future. If these investments pay off, they can significantly increase a company’s ROIC.
Now let’s consider the industrial gas business in relation to these levers:
Strategic Levers that impact the INDUSTRIAL GAS BUSINESS
The industrial gas industry involves the manufacture and distribution of gases like oxygen, nitrogen, argon, and carbon dioxide for use in various industries such as healthcare, food and beverage, metallurgy, and energy.
Operational efficiency is critical in this industry due to the high costs associated with producing and distributing industrial gases. Companies that can produce gases more efficiently or distribute them more cost-effectively will have a higher ROIC.
Capital structure also plays an important role in this industry. Industrial gas companies often require significant capital expenditure for building production facilities and distribution networks. Therefore, managing debt levels while ensuring sufficient equity financing is crucial for maintaining an optimal capital structure.
Tax efficiency is another important lever for industrial gas companies. These companies often operate in multiple jurisdictions with varying tax rates and regulations. Effective tax planning can help these companies minimize their tax liabilities and boost their ROIC.
Lastly, strategic investments are key for growth in this industry. Industrial gas companies need to continuously invest in new technologies and markets to stay competitive and drive future growth.
In conclusion, there are several levers that can impact the Return on Invested Capital (ROIC) of a company operating in any industry including the industrial gas business. By focusing on operational efficiency, maintaining an optimal capital structure, managing taxes effectively, and making strategic investments, companies can significantly enhance their ROIC.
Strategic Actions per Lever
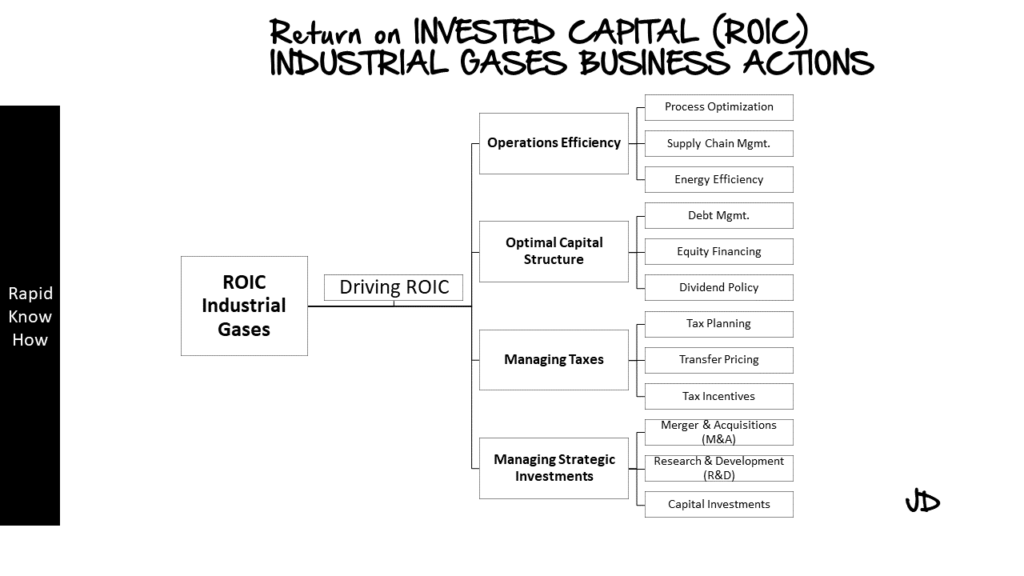
Industrial Gas: ROIC – 3 Strategic Actions per Lever
The Return on Invested Capital (ROIC) is a crucial financial metric that measures how efficiently a company generates profits from its capital investments. In the industrial gas sector, there are several strategic levers that can be pulled to improve ROIC. These include operational efficiency, optimal capital structure, managing tax efficiencies, and strategic management investments. Let’s delve into each of these levers and discuss three strategic actions that can be taken for each.
Lever 1: Operational Efficiency
Operational efficiency refers to the ability of a company to deliver products or services in the most cost-effective manner without sacrificing quality. Here are three strategic actions that can be taken:
1. Process Optimization: This involves streamlining operations to eliminate waste and redundancies. This could mean investing in automation technologies or implementing lean manufacturing principles.
2. Supply Chain Management: Efficient management of the supply chain can lead to significant cost savings. This could involve negotiating better terms with suppliers, improving inventory management, or optimizing logistics and distribution networks.
3. Energy Efficiency: Given the energy-intensive nature of industrial gas production, improving energy efficiency can lead to substantial cost savings. This could involve investing in energy-efficient equipment or implementing energy-saving practices at production facilities.
Lever 2: Optimal Capital Structure
The capital structure of a company refers to how it finances its operations and growth with different sources of funds, including debt and equity. Here are three strategic actions that can be taken:
1. Debt Management: This involves managing the level of debt in the capital structure to optimize interest costs while maintaining financial stability.
2. Equity Financing: This involves raising capital through issuing shares. While this can dilute existing shareholders’ ownership, it does not carry the same financial risk as debt.
3. Dividend Policy: The company’s dividend policy can also impact its capital structure. A balance needs to be struck between returning cash to shareholders and retaining enough funds for growth and investment.
Lever 3: Managing Tax Efficiencies
Tax efficiency refers to structuring business operations in a way that minimizes tax liabilities. Here are three strategic actions that can be taken:
1. Tax Planning: This involves understanding tax laws and regulations and planning business activities accordingly to minimize tax liabilities.
2. Transfer Pricing: For multinational industrial gas companies, transfer pricing – pricing transactions between company divisions in different countries – can be used as a tool for tax optimization.
3. Tax Incentives: Many governments offer tax incentives for certain activities such as research and development or investments in certain regions or industries. Companies should actively seek out such opportunities.
Lever 4: Management Strategic Investments
Strategic investments refer to long-term investments made by a company with the aim of achieving strategic objectives such as market expansion or diversification. Here are three strategic actions that can be taken:
1. Mergers & Acquisitions (M&A): M&A can provide opportunities for rapid expansion or entry into new markets.
2. Research & Development (R&D): Investment in R&D can lead to new products or technologies that provide a competitive advantage.
3. Capital Expenditure (CapEx): CapEx investments in new facilities or equipment can increase production capacity or improve operational efficiency.
In conclusion, improving ROIC requires a multi-faceted approach involving operational efficiency, optimal capital structure, tax efficiency, and strategic investments. By pulling these levers strategically, industrial gas companies can enhance their profitability and create value for their shareholders.
RIOC boosted from Virtual Assets
Return on Invested Capital (ROIC) is a financial metric that measures the profitability and value-creating potential of companies after considering the amount of capital invested. It is a crucial indicator for investors to understand how effectively a company uses its capital to generate profits. In the context of virtual assets, ROIC can be a significant determinant in assessing the impact on critical levers of the industrial gas industry, including operational efficiency, capital structure, tax efficiency, and strategic investments.
Operational Efficiency: Virtual assets can significantly enhance operational efficiency in the industrial gas industry. These assets, such as digital platforms or software solutions, can streamline processes, reduce manual labor, and minimize errors. For instance, predictive maintenance software can help identify potential equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime and saving costs. The increased operational efficiency can lead to higher profits without additional capital investment, thereby improving ROIC.
Capital Structure: Virtual assets can also influence a company’s capital structure. Traditionally, industrial gas companies have relied heavily on physical assets like plants and machinery. However, with the advent of digital transformation, there’s an increasing shift towards virtual assets like data analytics tools or AI-based systems. These assets often require less upfront capital than physical ones but can generate substantial returns over time. This shift can lower the company’s capital intensity (total assets/equity), leading to an improved ROIC.
Tax Efficiency: Virtual assets can also contribute to tax efficiency. For example, software or digital platforms are often classified as intangible assets for tax purposes. Depending on jurisdictional rules, companies may be able to amortize these assets over their useful life, leading to tax deductions that lower their effective tax rate. A lower tax rate means higher after-tax profits and thus a higher ROIC.
Strategic Investments: Lastly, virtual assets can play a pivotal role in strategic investments. Industrial gas companies that invest in these assets are likely positioning themselves for future growth opportunities. For instance, investing in blockchain technology could enable secure and transparent transactions across the supply chain. Or investing in data analytics could provide valuable insights into market trends and customer behavior. These strategic investments could lead to new revenue streams and higher profits in the long run, positively impacting ROIC.
In conclusion, virtual assets have the potential to significantly impact the critical levers of the industrial gas industry by enhancing operational efficiency, influencing capital structure decisions, improving tax efficiency and guiding strategic investments. By doing so, they can positively affect a company’s Return on Invested Capital (ROIC), making it an attractive proposition for investors.
Artifical Intelligence (AI) Applications for each Industrial Gas Lever
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been making waves across various industries, and the industrial gases sector is no exception. The integration of AI into this industry has brought about significant changes in operational efficiency, capital structuring, tax efficiency, and strategic investments.
Operational Efficiency:
AI has a profound impact on the operational efficiency of the industrial gases industry. It helps in streamlining processes, reducing downtime, and improving overall productivity. For instance, AI can predict equipment failures before they occur by analyzing data from sensors embedded in machinery. This predictive maintenance reduces unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs, thereby enhancing operational efficiency.
Moreover, AI can optimize logistics and supply chain management. It can analyze historical data to predict demand patterns and optimize inventory levels accordingly. This not only reduces storage costs but also ensures that the right products are available at the right time.
Capital Structuring:
AI also plays a crucial role in capital structuring in the industrial gases industry. It provides valuable insights into financial data, enabling companies to make informed decisions about capital allocation. For instance, AI algorithms can analyze market trends and predict future financial scenarios. This helps companies to structure their capital optimally, balancing between debt and equity based on predicted market conditions.
Tax Efficiency:
In terms of tax efficiency, AI can automate tax compliance processes, reducing errors and saving time. It can analyze tax regulations across different jurisdictions and apply them accurately to financial data. This not only ensures compliance with tax laws but also identifies opportunities for tax savings.
For example, AI can identify applicable tax credits or deductions that a company may not be aware of. It can also predict the impact of potential changes in tax laws on a company’s financial position. This proactive approach to tax management enhances tax efficiency and reduces risks associated with non-compliance.
Strategic Investments:
Finally, AI is transforming strategic investments in the industrial gases industry. It provides actionable insights into market trends, competitor strategies, customer behavior, and other relevant factors. These insights enable companies to make strategic investment decisions that align with their business objectives.
For instance, AI can identify potential investment opportunities in emerging markets or new technologies based on data analysis. It can also assess the risk associated with these investments by predicting potential challenges and returns.
In conclusion, AI is revolutionizing the industrial gases industry by enhancing operational efficiency, optimizing capital structure, improving tax efficiency, and guiding strategic investments. As AI technology continues to evolve, its impact on this industry is expected to grow even further.